Classifying MNIST digits using Logistic Regression¶
Note
This sections assumes familiarity with the following Theano concepts: shared variables , basic arithmetic ops , T.grad , floatX. If you intend to run the code on GPU also read GPU.
Note
The code for this section is available for download here.
In this section, we show how Theano can be used to implement the most basic classifier: the logistic regression. We start off with a quick primer of the model, which serves both as a refresher but also to anchor the notation and show how mathematical expressions are mapped onto Theano graphs.
In the deepest of machine learning traditions, this tutorial will tackle the exciting problem of MNIST digit classification.
The Model¶
Logistic regression is a probabilistic, linear classifier. It is parametrized by a weight matrix 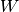 and a bias vector
and a bias vector 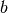 . Classification is done by projecting an input vector onto a set of hyperplanes, each of which corresponds to a class. The distance from the input to a hyperplane reflects the probability that the input is a member of the corresponding class.
. Classification is done by projecting an input vector onto a set of hyperplanes, each of which corresponds to a class. The distance from the input to a hyperplane reflects the probability that the input is a member of the corresponding class.
Mathematically, the probability that an input vector 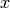 is a member of a class
is a member of a class 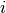 , a value of a stochastic variable
, a value of a stochastic variable 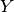 , can be written as:
, can be written as:
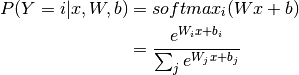
The model’s prediction 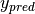 is the class whose probability is maximal, specifically:
is the class whose probability is maximal, specifically:

The code to do this in Theano is the following:
# initialize with 0 the weights W as a matrix of shape (n_in, n_out)
self.W = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_in, n_out),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='W',
borrow=True
)
# initialize the biases b as a vector of n_out 0s
self.b = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_out,),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='b',
borrow=True
)
# symbolic expression for computing the matrix of class-membership
# probabilities
# Where:
# W is a matrix where column-k represent the separation hyperplane for
# class-k
# x is a matrix where row-j represents input training sample-j
# b is a vector where element-k represent the free parameter of
# hyperplane-k
self.p_y_given_x = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)
# symbolic description of how to compute prediction as class whose
# probability is maximal
self.y_pred = T.argmax(self.p_y_given_x, axis=1)
Since the parameters of the model must maintain a persistent state throughout training, we allocate shared variables for 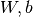 . This declares them both as being symbolic Theano variables, but also initializes their contents. The dot and softmax operators are then used to compute the vector
. This declares them both as being symbolic Theano variables, but also initializes their contents. The dot and softmax operators are then used to compute the vector 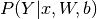 . The result
. The result p_y_given_x is a symbolic variable of vector-type.
To get the actual model prediction, we can use the T.argmax operator, which will return the index at which p_y_given_x is maximal (i.e. the class with maximum probability).
Now of course, the model we have defined so far does not do anything useful yet, since its parameters are still in their initial state. The following section will thus cover how to learn the optimal parameters.
Note
For a complete list of Theano ops, see: list of ops
Defining a Loss Function¶
Learning optimal model parameters involves minimizing a loss function. In the case of multi-class logistic regression, it is very common to use the negative log-likelihood as the loss. This is equivalent to maximizing the likelihood of the data set 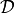 under the model parameterized by
under the model parameterized by 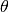 . Let us first start by defining the likelihood
. Let us first start by defining the likelihood 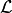 and loss
and loss  :
:
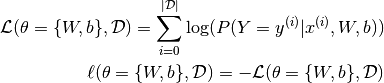
While entire books are dedicated to the topic of minimization, gradient descent is by far the simplest method for minimizing arbitrary non-linear functions. This tutorial will use the method of stochastic gradient method with mini-batches (MSGD). See Stochastic Gradient Descent for more details.
The following Theano code defines the (symbolic) loss for a given minibatch:
# y.shape[0] is (symbolically) the number of rows in y, i.e.,
# number of examples (call it n) in the minibatch
# T.arange(y.shape[0]) is a symbolic vector which will contain
# [0,1,2,... n-1] T.log(self.p_y_given_x) is a matrix of
# Log-Probabilities (call it LP) with one row per example and
# one column per class LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y] is a vector
# v containing [LP[0,y[0]], LP[1,y[1]], LP[2,y[2]], ...,
# LP[n-1,y[n-1]]] and T.mean(LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y]) is
# the mean (across minibatch examples) of the elements in v,
# i.e., the mean log-likelihood across the minibatch.
return -T.mean(T.log(self.p_y_given_x)[T.arange(y.shape[0]), y])
Note
Even though the loss is formally defined as the sum, over the data set, of individual error terms, in practice, we use the mean (T.mean) in the code. This allows for the learning rate choice to be less dependent of the minibatch size.
Creating a LogisticRegression class¶
We now have all the tools we need to define a LogisticRegression class, which encapsulates the basic behaviour of logistic regression. The code is very similar to what we have covered so far, and should be self explanatory.
class LogisticRegression(object):
"""Multi-class Logistic Regression Class
The logistic regression is fully described by a weight matrix :math:`W`
and bias vector :math:`b`. Classification is done by projecting data
points onto a set of hyperplanes, the distance to which is used to
determine a class membership probability.
"""
def __init__(self, input, n_in, n_out):
""" Initialize the parameters of the logistic regression
:type input: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param input: symbolic variable that describes the input of the
architecture (one minibatch)
:type n_in: int
:param n_in: number of input units, the dimension of the space in
which the datapoints lie
:type n_out: int
:param n_out: number of output units, the dimension of the space in
which the labels lie
"""
# start-snippet-1
# initialize with 0 the weights W as a matrix of shape (n_in, n_out)
self.W = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_in, n_out),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='W',
borrow=True
)
# initialize the biases b as a vector of n_out 0s
self.b = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_out,),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='b',
borrow=True
)
# symbolic expression for computing the matrix of class-membership
# probabilities
# Where:
# W is a matrix where column-k represent the separation hyperplane for
# class-k
# x is a matrix where row-j represents input training sample-j
# b is a vector where element-k represent the free parameter of
# hyperplane-k
self.p_y_given_x = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)
# symbolic description of how to compute prediction as class whose
# probability is maximal
self.y_pred = T.argmax(self.p_y_given_x, axis=1)
# end-snippet-1
# parameters of the model
self.params = [self.W, self.b]
# keep track of model input
self.input = input
def negative_log_likelihood(self, y):
"""Return the mean of the negative log-likelihood of the prediction
of this model under a given target distribution.
.. math::
\frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \mathcal{L} (\theta=\{W,b\}, \mathcal{D}) =
\frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \sum_{i=0}^{|\mathcal{D}|}
\log(P(Y=y^{(i)}|x^{(i)}, W,b)) \\
\ell (\theta=\{W,b\}, \mathcal{D})
:type y: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param y: corresponds to a vector that gives for each example the
correct label
Note: we use the mean instead of the sum so that
the learning rate is less dependent on the batch size
"""
# start-snippet-2
# y.shape[0] is (symbolically) the number of rows in y, i.e.,
# number of examples (call it n) in the minibatch
# T.arange(y.shape[0]) is a symbolic vector which will contain
# [0,1,2,... n-1] T.log(self.p_y_given_x) is a matrix of
# Log-Probabilities (call it LP) with one row per example and
# one column per class LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y] is a vector
# v containing [LP[0,y[0]], LP[1,y[1]], LP[2,y[2]], ...,
# LP[n-1,y[n-1]]] and T.mean(LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y]) is
# the mean (across minibatch examples) of the elements in v,
# i.e., the mean log-likelihood across the minibatch.
return -T.mean(T.log(self.p_y_given_x)[T.arange(y.shape[0]), y])
# end-snippet-2
def errors(self, y):
"""Return a float representing the number of errors in the minibatch
over the total number of examples of the minibatch ; zero one
loss over the size of the minibatch
:type y: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param y: corresponds to a vector that gives for each example the
correct label
"""
# check if y has same dimension of y_pred
if y.ndim != self.y_pred.ndim:
raise TypeError(
'y should have the same shape as self.y_pred',
('y', y.type, 'y_pred', self.y_pred.type)
)
# check if y is of the correct datatype
if y.dtype.startswith('int'):
# the T.neq operator returns a vector of 0s and 1s, where 1
# represents a mistake in prediction
return T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y))
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
We instantiate this class as follows:
# generate symbolic variables for input (x and y represent a
# minibatch)
x = T.matrix('x') # data, presented as rasterized images
y = T.ivector('y') # labels, presented as 1D vector of [int] labels
# construct the logistic regression class
# Each MNIST image has size 28*28
classifier = LogisticRegression(input=x, n_in=28 * 28, n_out=10)
We start by allocating symbolic variables for the training inputs 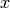 and their corresponding classes
and their corresponding classes 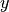 . Note that
. Note that x and y are defined outside the scope of the LogisticRegression object. Since the class requires the input to build its graph, it is passed as a parameter of the __init__ function. This is useful in case you want to connect instances of such classes to form a deep network. The output of one layer can be passed as the input of the layer above. (This tutorial does not build a multi-layer network, but this code will be reused in future tutorials that do.)
Finally, we define a (symbolic) cost variable to minimize, using the instance method classifier.negative_log_likelihood.
# the cost we minimize during training is the negative log likelihood of
# the model in symbolic format
cost = classifier.negative_log_likelihood(y)
Note that x is an implicit symbolic input to the definition of cost, because the symbolic variables of classifier were defined in terms of x at initialization.
Learning the Model¶
To implement MSGD in most programming languages (C/C++, Matlab, Python), one would start by manually deriving the expressions for the gradient of the loss with respect to the parameters: in this case 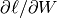 , and
, and 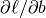 , This can get pretty tricky for complex models, as expressions for
, This can get pretty tricky for complex models, as expressions for 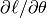 can get fairly complex, especially when taking into account problems of numerical stability.
can get fairly complex, especially when taking into account problems of numerical stability.
With Theano, this work is greatly simplified. It performs automatic differentiation and applies certain math transforms to improve numerical stability.
To get the gradients 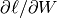 and
and 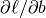 in Theano, simply do the following:
in Theano, simply do the following:
g_W = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.W)
g_b = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.b)
g_W and g_b are symbolic variables, which can be used as part of a computation graph. The function train_model, which performs one step of gradient descent, can then be defined as follows:
# specify how to update the parameters of the model as a list of
# (variable, update expression) pairs.
updates = [(classifier.W, classifier.W - learning_rate * g_W),
(classifier.b, classifier.b - learning_rate * g_b)]
# compiling a Theano function `train_model` that returns the cost, but in
# the same time updates the parameter of the model based on the rules
# defined in `updates`
train_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
updates is a list of pairs. In each pair, the first element is the symbolic variable to be updated in the step, and the second element is the symbolic function for calculating its new value. Similarly, givens is a dictionary whose keys are symbolic variables and whose values specify their replacements during the step. The function train_model is then defined such that:
- the input is the mini-batch index
indexthat, together with the batch size (which is not an input since it is fixed) defines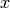 with corresponding labels
with corresponding labels - the return value is the cost/loss associated with the x, y defined by the
index - on every function call, it will first replace
xandywith the slices from the training set specified byindex. Then, it will evaluate the cost associated with that minibatch and apply the operations defined by theupdateslist.
Each time train_model(index) is called, it will thus compute and return the cost of a minibatch, while also performing a step of MSGD. The entire learning algorithm thus consists in looping over all examples in the dataset, considering all the examples in one minibatch at a time, and repeatedly calling the train_model function.
Testing the model¶
As explained in Learning a Classifier, when testing the model we are interested in the number of misclassified examples (and not only in the likelihood). The LogisticRegression class therefore has an extra instance method, which builds the symbolic graph for retrieving the number of misclassified examples in each minibatch.
The code is as follows:
def errors(self, y):
"""Return a float representing the number of errors in the minibatch
over the total number of examples of the minibatch ; zero one
loss over the size of the minibatch
:type y: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param y: corresponds to a vector that gives for each example the
correct label
"""
# check if y has same dimension of y_pred
if y.ndim != self.y_pred.ndim:
raise TypeError(
'y should have the same shape as self.y_pred',
('y', y.type, 'y_pred', self.y_pred.type)
)
# check if y is of the correct datatype
if y.dtype.startswith('int'):
# the T.neq operator returns a vector of 0s and 1s, where 1
# represents a mistake in prediction
return T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y))
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
We then create a function test_model and a function validate_model, which we can call to retrieve this value. As you will see shortly, validate_model is key to our early-stopping implementation (see Early-Stopping). These functions take a minibatch index and compute, for the examples in that minibatch, the number that were misclassified by the model. The only difference between them is that test_model draws its minibatches from the testing set, while validate_model draws its from the validation set.
# compiling a Theano function that computes the mistakes that are made by
# the model on a minibatch
test_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
validate_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y),
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
Putting it All Together¶
The finished product is as follows.
"""
This tutorial introduces logistic regression using Theano and stochastic
gradient descent.
Logistic regression is a probabilistic, linear classifier. It is parametrized
by a weight matrix :math:`W` and a bias vector :math:`b`. Classification is
done by projecting data points onto a set of hyperplanes, the distance to
which is used to determine a class membership probability.
Mathematically, this can be written as:
.. math::
P(Y=i|x, W,b) &= softmax_i(W x + b) \\
&= \frac {e^{W_i x + b_i}} {\sum_j e^{W_j x + b_j}}
The output of the model or prediction is then done by taking the argmax of
the vector whose i'th element is P(Y=i|x).
.. math::
y_{pred} = argmax_i P(Y=i|x,W,b)
This tutorial presents a stochastic gradient descent optimization method
suitable for large datasets.
References:
- textbooks: "Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning" -
Christopher M. Bishop, section 4.3.2
"""
from __future__ import print_function
__docformat__ = 'restructedtext en'
import six.moves.cPickle as pickle
import gzip
import os
import sys
import timeit
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T
class LogisticRegression(object):
"""Multi-class Logistic Regression Class
The logistic regression is fully described by a weight matrix :math:`W`
and bias vector :math:`b`. Classification is done by projecting data
points onto a set of hyperplanes, the distance to which is used to
determine a class membership probability.
"""
def __init__(self, input, n_in, n_out):
""" Initialize the parameters of the logistic regression
:type input: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param input: symbolic variable that describes the input of the
architecture (one minibatch)
:type n_in: int
:param n_in: number of input units, the dimension of the space in
which the datapoints lie
:type n_out: int
:param n_out: number of output units, the dimension of the space in
which the labels lie
"""
# start-snippet-1
# initialize with 0 the weights W as a matrix of shape (n_in, n_out)
self.W = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_in, n_out),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='W',
borrow=True
)
# initialize the biases b as a vector of n_out 0s
self.b = theano.shared(
value=numpy.zeros(
(n_out,),
dtype=theano.config.floatX
),
name='b',
borrow=True
)
# symbolic expression for computing the matrix of class-membership
# probabilities
# Where:
# W is a matrix where column-k represent the separation hyperplane for
# class-k
# x is a matrix where row-j represents input training sample-j
# b is a vector where element-k represent the free parameter of
# hyperplane-k
self.p_y_given_x = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b)
# symbolic description of how to compute prediction as class whose
# probability is maximal
self.y_pred = T.argmax(self.p_y_given_x, axis=1)
# end-snippet-1
# parameters of the model
self.params = [self.W, self.b]
# keep track of model input
self.input = input
def negative_log_likelihood(self, y):
"""Return the mean of the negative log-likelihood of the prediction
of this model under a given target distribution.
.. math::
\frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \mathcal{L} (\theta=\{W,b\}, \mathcal{D}) =
\frac{1}{|\mathcal{D}|} \sum_{i=0}^{|\mathcal{D}|}
\log(P(Y=y^{(i)}|x^{(i)}, W,b)) \\
\ell (\theta=\{W,b\}, \mathcal{D})
:type y: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param y: corresponds to a vector that gives for each example the
correct label
Note: we use the mean instead of the sum so that
the learning rate is less dependent on the batch size
"""
# start-snippet-2
# y.shape[0] is (symbolically) the number of rows in y, i.e.,
# number of examples (call it n) in the minibatch
# T.arange(y.shape[0]) is a symbolic vector which will contain
# [0,1,2,... n-1] T.log(self.p_y_given_x) is a matrix of
# Log-Probabilities (call it LP) with one row per example and
# one column per class LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y] is a vector
# v containing [LP[0,y[0]], LP[1,y[1]], LP[2,y[2]], ...,
# LP[n-1,y[n-1]]] and T.mean(LP[T.arange(y.shape[0]),y]) is
# the mean (across minibatch examples) of the elements in v,
# i.e., the mean log-likelihood across the minibatch.
return -T.mean(T.log(self.p_y_given_x)[T.arange(y.shape[0]), y])
# end-snippet-2
def errors(self, y):
"""Return a float representing the number of errors in the minibatch
over the total number of examples of the minibatch ; zero one
loss over the size of the minibatch
:type y: theano.tensor.TensorType
:param y: corresponds to a vector that gives for each example the
correct label
"""
# check if y has same dimension of y_pred
if y.ndim != self.y_pred.ndim:
raise TypeError(
'y should have the same shape as self.y_pred',
('y', y.type, 'y_pred', self.y_pred.type)
)
# check if y is of the correct datatype
if y.dtype.startswith('int'):
# the T.neq operator returns a vector of 0s and 1s, where 1
# represents a mistake in prediction
return T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y))
else:
raise NotImplementedError()
def load_data(dataset):
''' Loads the dataset
:type dataset: string
:param dataset: the path to the dataset (here MNIST)
'''
#############
# LOAD DATA #
#############
# Download the MNIST dataset if it is not present
data_dir, data_file = os.path.split(dataset)
if data_dir == "" and not os.path.isfile(dataset):
# Check if dataset is in the data directory.
new_path = os.path.join(
os.path.split(__file__)[0],
"..",
"data",
dataset
)
if os.path.isfile(new_path) or data_file == 'mnist.pkl.gz':
dataset = new_path
if (not os.path.isfile(dataset)) and data_file == 'mnist.pkl.gz':
from six.moves import urllib
origin = (
'http://www.iro.umontreal.ca/~lisa/deep/data/mnist/mnist.pkl.gz'
)
print('Downloading data from %s' % origin)
urllib.request.urlretrieve(origin, dataset)
print('... loading data')
# Load the dataset
with gzip.open(dataset, 'rb') as f:
try:
train_set, valid_set, test_set = pickle.load(f, encoding='latin1')
except:
train_set, valid_set, test_set = pickle.load(f)
# train_set, valid_set, test_set format: tuple(input, target)
# input is a numpy.ndarray of 2 dimensions (a matrix)
# where each row corresponds to an example. target is a
# numpy.ndarray of 1 dimension (vector) that has the same length as
# the number of rows in the input. It should give the target
# to the example with the same index in the input.
def shared_dataset(data_xy, borrow=True):
""" Function that loads the dataset into shared variables
The reason we store our dataset in shared variables is to allow
Theano to copy it into the GPU memory (when code is run on GPU).
Since copying data into the GPU is slow, copying a minibatch everytime
is needed (the default behaviour if the data is not in a shared
variable) would lead to a large decrease in performance.
"""
data_x, data_y = data_xy
shared_x = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_x,
dtype=theano.config.floatX),
borrow=borrow)
shared_y = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_y,
dtype=theano.config.floatX),
borrow=borrow)
# When storing data on the GPU it has to be stored as floats
# therefore we will store the labels as ``floatX`` as well
# (``shared_y`` does exactly that). But during our computations
# we need them as ints (we use labels as index, and if they are
# floats it doesn't make sense) therefore instead of returning
# ``shared_y`` we will have to cast it to int. This little hack
# lets ous get around this issue
return shared_x, T.cast(shared_y, 'int32')
test_set_x, test_set_y = shared_dataset(test_set)
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = shared_dataset(valid_set)
train_set_x, train_set_y = shared_dataset(train_set)
rval = [(train_set_x, train_set_y), (valid_set_x, valid_set_y),
(test_set_x, test_set_y)]
return rval
def sgd_optimization_mnist(learning_rate=0.13, n_epochs=1000,
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz',
batch_size=600):
"""
Demonstrate stochastic gradient descent optimization of a log-linear
model
This is demonstrated on MNIST.
:type learning_rate: float
:param learning_rate: learning rate used (factor for the stochastic
gradient)
:type n_epochs: int
:param n_epochs: maximal number of epochs to run the optimizer
:type dataset: string
:param dataset: the path of the MNIST dataset file from
http://www.iro.umontreal.ca/~lisa/deep/data/mnist/mnist.pkl.gz
"""
datasets = load_data(dataset)
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1]
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
# compute number of minibatches for training, validation and testing
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] // batch_size
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] // batch_size
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] // batch_size
######################
# BUILD ACTUAL MODEL #
######################
print('... building the model')
# allocate symbolic variables for the data
index = T.lscalar() # index to a [mini]batch
# generate symbolic variables for input (x and y represent a
# minibatch)
x = T.matrix('x') # data, presented as rasterized images
y = T.ivector('y') # labels, presented as 1D vector of [int] labels
# construct the logistic regression class
# Each MNIST image has size 28*28
classifier = LogisticRegression(input=x, n_in=28 * 28, n_out=10)
# the cost we minimize during training is the negative log likelihood of
# the model in symbolic format
cost = classifier.negative_log_likelihood(y)
# compiling a Theano function that computes the mistakes that are made by
# the model on a minibatch
test_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
validate_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y),
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
# compute the gradient of cost with respect to theta = (W,b)
g_W = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.W)
g_b = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.b)
# start-snippet-3
# specify how to update the parameters of the model as a list of
# (variable, update expression) pairs.
updates = [(classifier.W, classifier.W - learning_rate * g_W),
(classifier.b, classifier.b - learning_rate * g_b)]
# compiling a Theano function `train_model` that returns the cost, but in
# the same time updates the parameter of the model based on the rules
# defined in `updates`
train_model = theano.function(
inputs=[index],
outputs=cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
# end-snippet-3
###############
# TRAIN MODEL #
###############
print('... training the model')
# early-stopping parameters
patience = 5000 # look as this many examples regardless
patience_increase = 2 # wait this much longer when a new best is
# found
improvement_threshold = 0.995 # a relative improvement of this much is
# considered significant
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience // 2)
# go through this many
# minibatche before checking the network
# on the validation set; in this case we
# check every epoch
best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
done_looping = False
epoch = 0
while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping):
epoch = epoch + 1
for minibatch_index in range(n_train_batches):
minibatch_avg_cost = train_model(minibatch_index)
# iteration number
iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index
if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0:
# compute zero-one loss on validation set
validation_losses = [validate_model(i)
for i in range(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses)
print(
'epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, validation error %f %%' %
(
epoch,
minibatch_index + 1,
n_train_batches,
this_validation_loss * 100.
)
)
# if we got the best validation score until now
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss:
#improve patience if loss improvement is good enough
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * \
improvement_threshold:
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase)
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss
# test it on the test set
test_losses = [test_model(i)
for i in range(n_test_batches)]
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses)
print(
(
' epoch %i, minibatch %i/%i, test error of'
' best model %f %%'
) %
(
epoch,
minibatch_index + 1,
n_train_batches,
test_score * 100.
)
)
# save the best model
with open('best_model.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(classifier, f)
if patience <= iter:
done_looping = True
break
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print(
(
'Optimization complete with best validation score of %f %%,'
'with test performance %f %%'
)
% (best_validation_loss * 100., test_score * 100.)
)
print('The code run for %d epochs, with %f epochs/sec' % (
epoch, 1. * epoch / (end_time - start_time)))
print(('The code for file ' +
os.path.split(__file__)[1] +
' ran for %.1fs' % ((end_time - start_time))), file=sys.stderr)
def predict():
"""
An example of how to load a trained model and use it
to predict labels.
"""
# load the saved model
classifier = pickle.load(open('best_model.pkl'))
# compile a predictor function
predict_model = theano.function(
inputs=[classifier.input],
outputs=classifier.y_pred)
# We can test it on some examples from test test
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz'
datasets = load_data(dataset)
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
test_set_x = test_set_x.get_value()
predicted_values = predict_model(test_set_x[:10])
print("Predicted values for the first 10 examples in test set:")
print(predicted_values)
if __name__ == '__main__':
sgd_optimization_mnist()
The user can learn to classify MNIST digits with SGD logistic regression, by typing, from within the DeepLearningTutorials folder:
python code/logistic_sgd.py
The output one should expect is of the form :
...
epoch 72, minibatch 83/83, validation error 7.510417 %
epoch 72, minibatch 83/83, test error of best model 7.510417 %
epoch 73, minibatch 83/83, validation error 7.500000 %
epoch 73, minibatch 83/83, test error of best model 7.489583 %
Optimization complete with best validation score of 7.500000 %,with test performance 7.489583 %
The code run for 74 epochs, with 1.936983 epochs/sec
On an Intel(R) Core(TM)2 Duo CPU E8400 @ 3.00 Ghz the code runs with approximately 1.936 epochs/sec and it took 75 epochs to reach a test error of 7.489%. On the GPU the code does almost 10.0 epochs/sec. For this instance we used a batch size of 600.
Prediction Using a Trained Model¶
sgd_optimization_mnist serialize and pickle the model each time new lowest validation error is reached. We can reload this model and predict labels of new data. predict function shows an example of how this could be done.
def predict():
"""
An example of how to load a trained model and use it
to predict labels.
"""
# load the saved model
classifier = pickle.load(open('best_model.pkl'))
# compile a predictor function
predict_model = theano.function(
inputs=[classifier.input],
outputs=classifier.y_pred)
# We can test it on some examples from test test
dataset='mnist.pkl.gz'
datasets = load_data(dataset)
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
test_set_x = test_set_x.get_value()
predicted_values = predict_model(test_set_x[:10])
print("Predicted values for the first 10 examples in test set:")
print(predicted_values)
Footnotes
| [1] | For smaller datasets and simpler models, more sophisticated descent algorithms can be more effective. The sample code logistic_cg.py demonstrates how to use SciPy’s conjugate gradient solver with Theano on the logistic regression task. |