SynthesizRR:通过检索增强生成多样化的数据集
摘要
由于计算和内存限制,通常需要将大型语言模型(大语言模型)的功能提炼成较小的学生模型。 对于分类任务执行此操作的一种方法是通过数据集合成,这可以通过从大语言模型生成每个标签的示例来完成。 先前的综合方法使用少样本提示,它依赖于大语言模型的参数知识来生成可用的示例。 然而,这会导致重复、对流行实体的偏见以及与人类文本的风格差异等问题。 在这项工作中,我们提出通过检索和细化进行合成(SynthesizRR),它使用检索增强将多样性引入数据集合成过程:随着检索到的段落变化,大语言模型被“播种”不同的内容。内容来生成其示例。 我们实证研究了六个数据集的合成,涵盖主题分类、情感分析、语气检测和幽默,需要复杂的合成策略。 我们发现SynthesizRR111https://github.com/amazon-science/synthesizrr 极大地提高了词汇和语义多样性、与人类编写文本的相似性以及蒸馏性能。
SynthesizRR:通过检索增强生成多样化数据集
Abhishek Divekar††thanks: Work completed while at Amazon. Greg Durrett Amazon Department of Computer Science, The University of Texas at Austin adivekar@amazon.com gdurrett@cs.utexas.edu
1简介
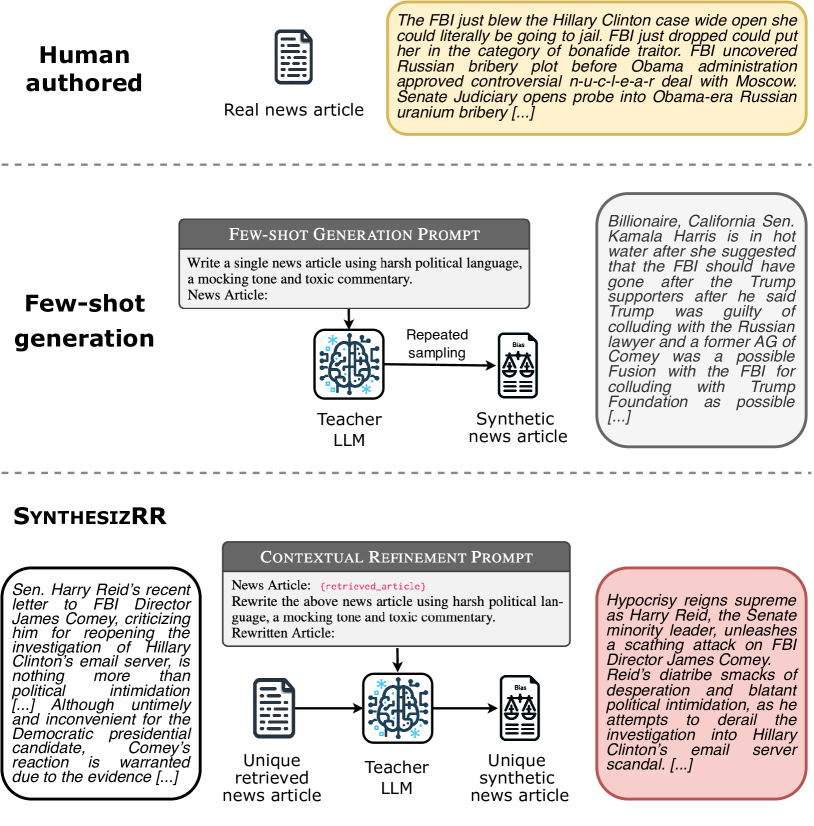
大语言模型,例如GPT-4 (OpenAI, 2023; Bubeck 等人, 2023)、LLaMa (Touvron 等人, 2023b) 和 Claude (Bai 等人, 2022) 是多用途的通才模型,能够解决多个问题无需通过零样本或少样本提示进行参数调整的任务。 相比之下,之前的方法在特定任务演示上微调 BERT 变体(Devlin 等人,2019),产生专家 模型。 这些较小的专业模型在推理时更经济,但需要至少数千个示例来训练。
最近的工作试图通过师生蒸馏(West等人,2022)对合成数据集上的专家模型进行微调,从而避免这种对手动创建示例的依赖。 这在分类(Yu 等人, 2023a; Ye 等人, 2022a, b)、人类偏好对齐(Lee 等人, 2023; Bai 等人, 2022)方面有应用。 t1>、语言理解(Meng 等人,2022;Schick 和 Schütze,2021),甚至表格数据(Borisov 等人,2022)。 然而,合成数据有局限性。 正如 Yu 等人 (2023a) 所指出的,幼稚的提示生成的文本多样性有限,反映了教师大语言模型的偏见。
Figure 1说明了少样本合成方法(Ye 等人, 2022a, b; Yehudai 等人, 2024a),我们将其称为FewGen,用于检测带有政治偏见的文章的任务。 通过适当的提示和上下文示例,从大语言模型中采样延续会以我们试图检测的有偏见的风格生成可信的新闻。 然而,当从固定提示中采样数千个完成时,我们观察到重复、对流行实体的偏见以及与人类书写文本的风格差异。 从如此低多样性的数据集中提取的专业模型可能无法很好地学习该任务。
在这项工作中,我们寻求缓解合成数据缺乏多样性的问题。 我们建议数据集合成可以分解为两种不同的大语言模型能力:内容源,其中大语言模型获取任务的相关信息,以及任务反转,其中大语言模型使用目标条件提示生成合成输入。 先前的工作主要集中在任务反转,同时隐式地使用大语言模型的参数记忆来进行内容采购。 相反,我们研究了显式内容采购阶段的重要性。
我们提出通过检索和细化进行合成 (SynthesizRR),这是一个由检索语料库指导的示例合成过程。 在内容采购步骤中,我们使用上下文学习协变量作为检索查询,从特定领域的语料库中每个查询提取数十个文档。 随后,多面手大语言模型对每个检索到的文档执行任务反转。 由于每个提示都使用唯一的检索文档,因此我们的综合过程会生成不同的示例,并丰富了广泛的现实世界实体和断言。
我们在六个文本分类任务上对 SynthesizRR 与 FewGen 进行基准测试,这些任务经过精心挑选,以衡量各种不同风格的数据集合成。 我们的实验 (§5) 表明 SynthesizRR 在多样性和与人类创作文本的相似性方面显着超过 FewGen,尽管两个程序都使用相同的程序冰冻大语言模型。 在§6中,我们看到在 SynthesizRR 生成的数据上微调的学生分类器比在 FewGen 上微调的学生分类器表现更好。 最后,在§7中,我们将 SynthesizRR 与四种最先进的分类数据集合成方法进行比较,发现 SynthesizRR 提供了更高多样性的数据集,更好地匹配人类编写的实例,并在大多数情况下提高学生的准确性。
我们的贡献如下:(1)我们提出了一种用于师生蒸馏的示例合成新方法,该方法基于使用检索语料库的任务反转步骤; (2) 我们引入 SynthesizRR RetrICL 算法来为我们的方法创建一个真实的上下文学习集; (3)我们实证分析了六种具有挑战性的分类任务的综合,将我们的方法的文本多样性和相似性以及下游任务的准确性与现有方法进行比较; (4) 我们通过改变监督数据量、语料库与任务的相关性、上下文示例的数量以及稀疏与密集检索来查明影响合成数据集质量的因素。
2 后台和任务设置
在本文中,我们重点关注为具有挑战性的文本分类任务生成数据集。 将一个示例表示为由输入文本 和 类的输出空间 的输出 组成。 我们的目标是生成一个合成数据集并训练一个专业语言模型(例如BERT风格的预训练模型(Devlin等人,2019))。 我们通过 任务反转创建 :反复提示教师语言模型 ,以生成给定相应标签 的合成协变量 。 我们将学生任务(根据预测)表示为,将教师任务(生成 (给定 )作为 。
SynthesizRR 旨在通过在内容采购步骤中利用检索来解决缺乏多样性的问题。 我们假设存在一个语料库,其中每个文档都可以保存与任务相关的信息。 然而,文档不需要来自与我们的任务协变量相同的分布;即使是关系较远的文档也可以产生有价值的综合示例。 例如,我们展示了我们可以从产品描述语料库中成功生成评论和幽默问题。 我们还假设可以访问示例 的种子集,该种子集足够大以表示类,但又足够小以供用户在几个小时内手动编译;在实验中,我们使用上下文学习集。 重要的是,我们假设种子集不足以训练有效的学生,并且需要更大的 ()。
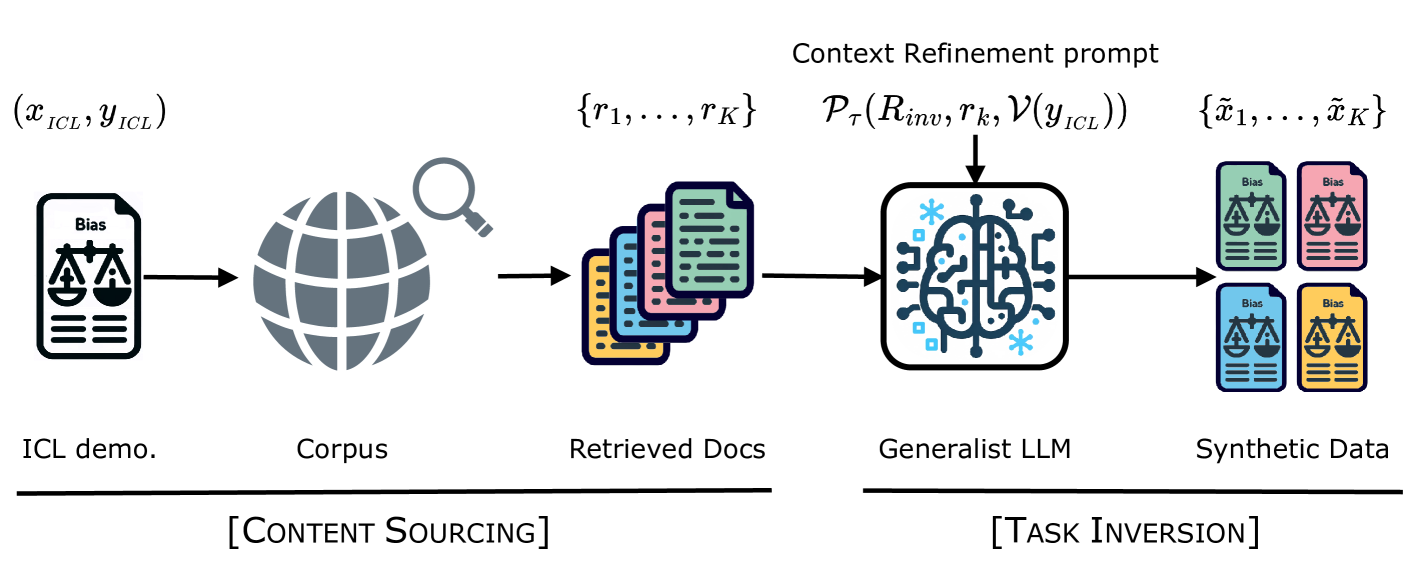
Figure 2 说明了我们生成分布相似协变量的方法。 最初,我们根据 中的示例检索文档,假设语料库包含足够的领域相似文档。 然后,我们构建一个上下文细化指令来对每个检索到的文档执行任务反转。 这种方法为大语言模型提供了每个生成示例的独特且有根据的提示,从而避免了教师大语言模型在其有限参数内记忆大量语料数据的需要。 由于检索到的文档和测试示例之间不匹配,任务反演可能具有挑战性;为了克服这个问题,我们将我们的调查限制在表现出强大的指令跟随能力的教师大语言模型(Ouyang等人,2022;Touvron等人,2023b;Bai等人,2022)。
3方法
算法 1 显示了我们的数据集生成方法。 我们通过以下步骤提取学生模型:
步骤1。 使用检索进行内容采购: SynthesizRR 使用每个上下文协变量 作为信息检索的查询,以及其在上下文学习期间的后续角色。 对于每个查询,我们使用密集检索器 检索 cosing 相似度逐渐降低的 文档 。 我们保留 (0.4, 0.9), 中具有余弦相似度的文档,以确保最小相似度,同时排除过于相似的文档作为 的潜在重复项。 每个生成的三元组 都会附加到集合 中。
第2步。 上下文集合构建: 随后的任务反转步骤也受益于上下文演示,但构建有效捕获上下文细化任务的演示具有挑战性。 我们探索了两种情境学习方法。
1. RetrICL: 我们使用检索来构造一组 ICL 示例 ,以便每个 ICL 示例都反映我们的任务反转提示的格式。 我们从密集检索结果中选择top-1和top-2检索结果,并使用余弦相似度标准来评估检索文档和。 尽管上下文对可能不完全匹配,但它们按照Appendix H 演示了所需的格式。
2. 非 RetrICL: 基线方法,它使用检索来获取内容,但不用于上下文学习。 对于每一代,我们从 中随机选择 ICL 示例。 每个示例都附加了诸如 “新闻文章:” 或 “产品详细信息:” 之类的前缀,但我们不添加上下文细化指令。 在 ICL 示例之后,我们附加检索到的文档 和上下文细化指令 以形成最终提示。 这种格式与 FewGen 使用的上下文学习提示密切相关,但也包含内容源元素 和 。 此基线突出显示了通过在 RetrICL 方法中构造 所增加的价值。
步骤 3. 使用上下文细化的任务反转: 任务反转提示的最小元素是上下文细化指令和目标。 我们使用语言器函数 (Schick and Schütze, 2021; van de Kar 等人, 2022) 来提供每个标签的唯一文本表示,即 。 我们遵循基于分类的任务反转的先前工作(Schick and Schütze,2021;Ye 等人,2022a,b;Yu 等人,2023b;Gao 等人,2023)并使用描述性语言来归纳最终数据集中的标签可分离性。
FewGen 使用标准因果语言建模目标从教师大语言模型 中导出下一个标记概率。 核采样Holtzman et al. (2019)用于对下一个词符进行自回归采样,直到生成<eos>词符。 这成为合成示例。
| (1) |
对于每个标签 ,我们修复此提示并采样 次以生成合成数据集。
在 SynthesizRR 中,我们根据 中的每个三元组创建合成数据集。 检索到的文档 与查询 具有词汇和语义重叠。 然而,由于文档或分块过程的性质,语料库文档在分布上可能与实际任务协变量不同(Mialon 等人,2023)。 为了解决这个问题,我们使用 根据每个检索到的文档的内容执行任务反转,我们将这个过程称为上下文细化。 因此由上下文细化指令 、每个文档 以及查询的语言化目标(即 )组成。 因此,当自动回归生成每个合成输入 时,大语言模型的上下文窗口会看到一个独特且扎实的提示:
| (2) |
对于所有文档。 我们继续使用细胞核取样来获得不同的世代。 因此,每个原始上下文示例都会产生 独特的合成示例 ;我们将 称为“扩展因子”。 为了促进对 的遵守,我们对 中的样本对进行采样,以创建遵循相同格式的上下文示例。 我们的最终数据集构造为:
。
步骤4。 学生蒸馏: 学生通过前馈层传递 的 BERT [CLS] 词符嵌入来对 进行微调。 这会产生标签空间 上的概率分布。我们优化真实标签的交叉熵损失。 由于我们从老师大语言模型中衍生出,这可以被认为是一种符号知识蒸馏(West等人,2022)的形式。
| Dataset | Class | Train, Test | Corpus | Difficulty | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AG News | 4 | RN/Dom | Easy | |||
| ToI Headlines | 10 | RN/Ind | Easy | |||
| Hyperpartisan | 2 | RN/Dom | Medium | |||
| Polarity | 2 | Products | Medium | |||
| Category | 23 | Products | Medium | |||
| Humor | 2 | Products | Hard | |||
| IMDb | 2 | Movies | Medium | |||
| SST-2 | 2 | Movies | Medium |
4实验设置
任务及其难度。 我们在Table 1中的前6个数据集上进行了主要实验,这些数据集经过精心挑选,以衡量教师大语言模型在不同难度的任务反转任务上的表现。 之前的工作仅对情感和主题分类数据集进行基准测试,例如 IMDb Maas 等人 (2011) 和 AG News (Zhang 等人, 2015 )。 我们从主题分类进行扩展,主要涉及任务反转步骤中的摘要,而大语言模型擅长(Goyal等人,2022)。 Hyperpartisan (Kiesel 等人, 2019) 检测政治新闻中的偏见,因此任务反转步骤包括对中性检索到的文章进行更实质性的重写,以形成有偏见的示例。 类别和极性是常见的产品审核任务(Yu等人,2023a,b;Gao等人,2023);我们从检索到的产品中生成评论,这些评论必须符合分类和情感类别。 幽默(Ziser等人,2020)的任务反转涉及从检索到的产品详细信息生成幽默问题,这需要教师具备额外的技能。 所有任务的提示均位于Appendix H 中。
| Corpus | Domain | Size | Doc. | Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RealNews/Dom | US/EU News | Article | ||
| RealNews/Reg | Regional News | Article | ||
| RealNews/Ind | Indian News | Article | ||
| Products | E-commerce | Product | ||
| Movie Summary | Movies | Plot |
Table 2描述了用于检索的语料库。 我们考虑不同领域的五个语料库,每个语料库都有不同数量的记录。 其中三个是 RealNews (Zellers 等人, 2019) 的子集,如Appendix J 中所述:RealNews/Dominant (美国/欧盟新闻)、RealNews/Regional(地区新闻)、RealNews/India(印度新闻)。 我们还使用产品(亚马逊产品元数据,(Ni等人,2019))和电影摘要(电影摘要,(Bamman等人,2013)。 Table 1 中的每个任务都与我们认为最相关的语料库相关联。 在§7中,我们在其他三个任务上与四种先前方法进行了比较:IMDb Maas 等人 (2011)、SST-2 Socher 等人 (2013) 和 AG News。 这些情绪和主题任务与我们的目标不太一致,因此被排除在我们的主要评估之外。
| Method | Example |
|---|---|
| Gold | There is decent bass, but the highs are a bit soft. A quick tweak to my equalizer, and they’re great. After reading several of the reviews on Amazon, I was a bit worried about the sound, but now that I have them I’m very happy. They’re a good price, and sooooo much better than the little ipod-like earbuds I’ve tried before. Those never stayed in my ear, and the bass never made me happy. |
| FewGen | I’ve been a very happy customer of this company for a long time. It is fast and does everything I need it to. I would definitely recommend it to anyone looking for a good external drive. However, I do have one issue with the product. The instructions that come with it are not very clear and I had a hard time figuring out how to properly use it. |
| (Retrieved Product) | Portable Laptop Microphone. Connects to 1/8" mini microphone input on laptop. Right-angle shaped. Flat-frequency response. |
| SynthesizRR | The portable laptop microphone is right-angled and has a flat-frequency response, making it easy to use for online meetings and interviews. It connects to the 1/8" mini microphone input on my laptop and has worked great for the past two months, but I have noticed some distortion in the audio when I move around too much. Overall, it’s a great value for the price and has made my remote work and video conferencing much more productive and efficient. |
型号。 我们使用 Contriever (Izacard 等人, 2022) 对每个语料库进行密集检索。 这使用余弦相似度在查询和每个文档之间执行语义匹配。 在Appendix F中,我们还使用BM25作为稀疏检索器进行消融研究,它在每个查询-文档对之间进行词汇匹配。
作为教师模型,我们主要使用冻结的Llama-2 Chat 13B (Touvron等人,2023b)来进行SynthesizRR 和 FewGen。 我们还按照Appendix K 中所述对 Claude Instant-v1 进行实验。对于上下文学习 (ICL) Brown 等人 (2020),我们从训练集中随机选择示例:对于多类任务,每类 50 个 ICL 示例,对于二元任务,每类 100 个示例。 我们相信,如果系统设计者付出一些努力来构建专业模型,他们就可以找到这些现实的例子。 我们探索在有限监督设置Appendix D 中引导该种子集的方法。
专业化表现是在学生 LM DeBERTa-v3-Large(435M 参数,He 等人 (2021))和 DistilBERT (66M 参数,Sanh 等人 (2019))。
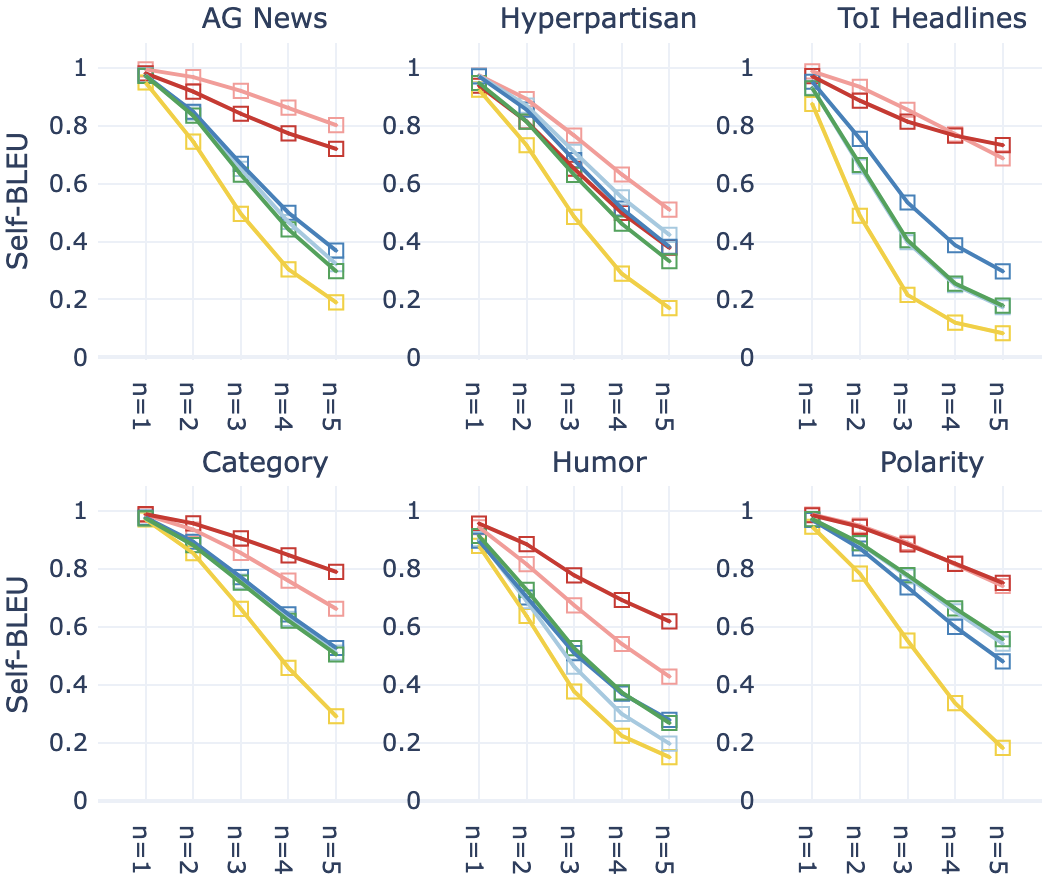
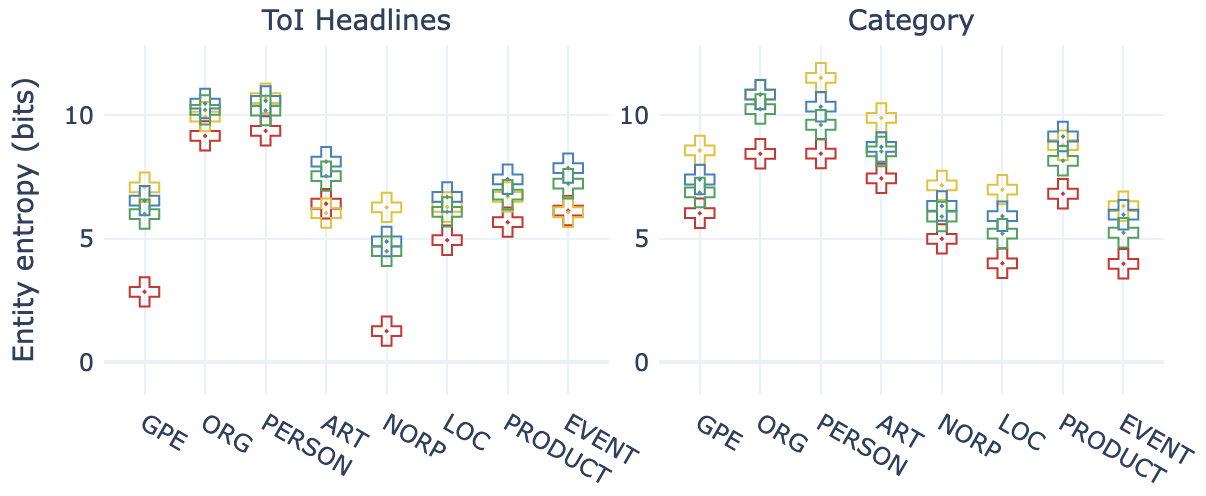
评价标准。 在多任务场景中客观评估文本生成可能具有挑战性(Chang 等人,2024)。 因此,在§5中,我们根据几个标准评估合成文本,以检测我们在合成过程中观察到的行为,如Table 3中所示。 Self-BLEU (Papineni 等人, 2002; Zhu 等人, 2018) 基于对之间的语法重叠来衡量数据集的词汇多样性的例子。 实体熵使用16种实体类型中每种实体类型的概率分布来测量实体的多样性,这是使用spaCy的en_core_web_lg(Honnibal等推断出来的)人,2020)。 过度代表流行实体的数据集在熵上得分较低。 另一方面,实体召回率和实体 KL 散度将实体的相似度与Gold和数据集进行比较再现 Gold 数据中常见的实体得分更高。 MAUVE (Liu 等人, 2021) 通过使用 gpt2-xl 模型的预训练表示来测量与人类书写文本的相似性,表明生成文本中的分布差异。
| Method | Norp | Org | Person | Gpe | Recall | KL div. |
| Unique Entities | ||||||
| Gold | 319 | 3943 | 3952 | 712 | - | - |
| FewGen* | 43 | 480 | 400 | 73 | 0.05 | - |
| SynzthRR† | 137 | 2718 | 1528 | 238 | 0.12 | - |
| SynzthRR‡ | 109 | 1755 | 1012 | 178 | 0.10 | - |
| Total Entities | ||||||
| Gold | 843 | 7233 | 6096 | 1558 | - | - |
| FewGen* | 94 | 775 | 506 | 96 | 0.23 | 3.10 |
| SynzthRR† | 319 | 3991 | 1989 | 397 | 0.35 | 2.35 |
| SynzthRR‡ | 314 | 2699 | 1464 | 363 | 0.32 | 2.52 |
5 结果:内在评估
在本节中,我们重点评估生成的数据集的内在属性,包括其多样性和实体覆盖率。 我们关注LLaMa-2 Chat 13B教师大语言模型,使用Table 1的语料库从Contriever进行检索(我们分析了Appendix E 我们生成的数据集的大小与 Gold 行数相关:K 行(AG News、ToI Headlines 、类别)、K 行(极性)或 K 行(超党派、 幽默)。 示例生成位于Appendix I 中。
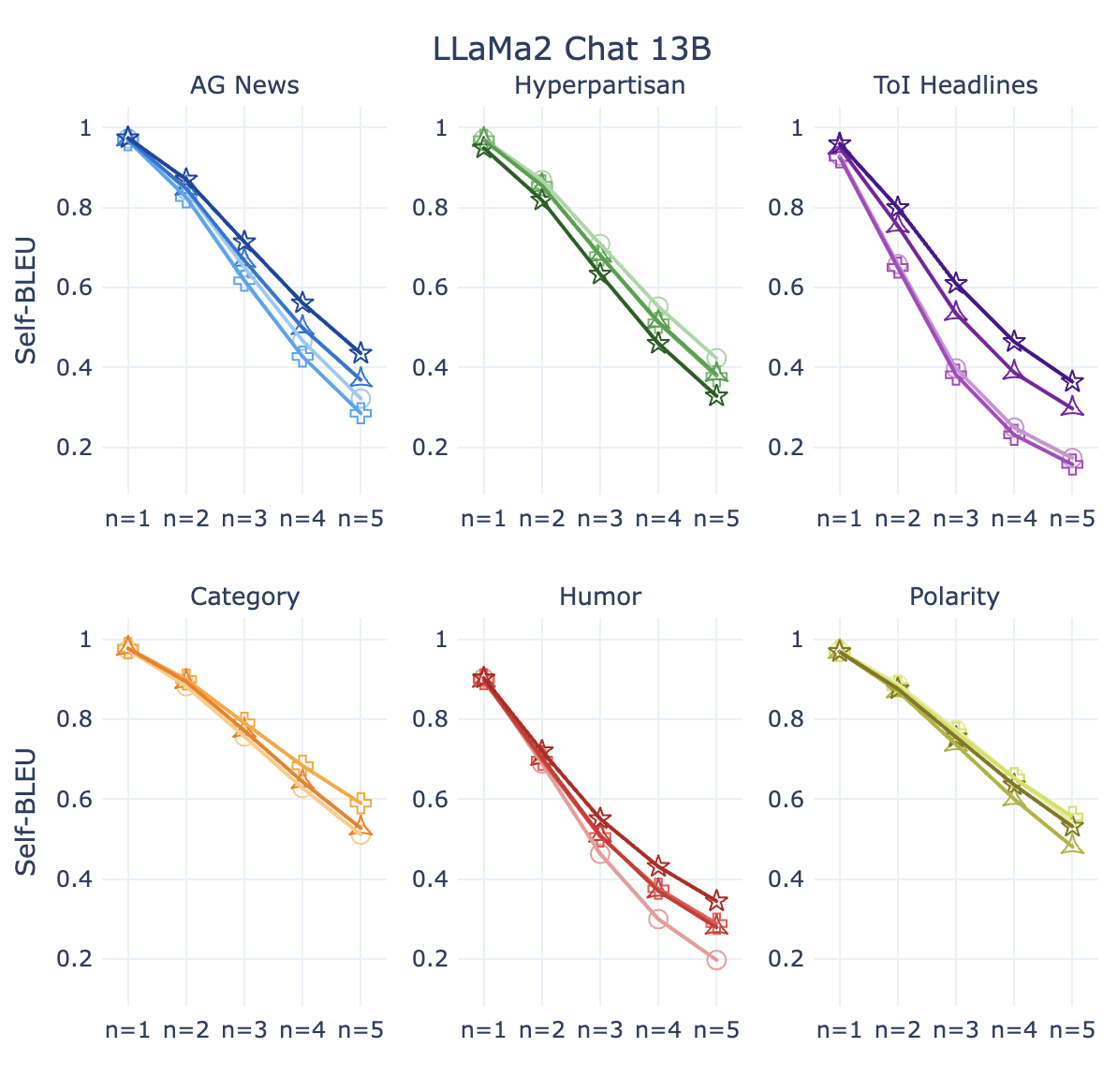
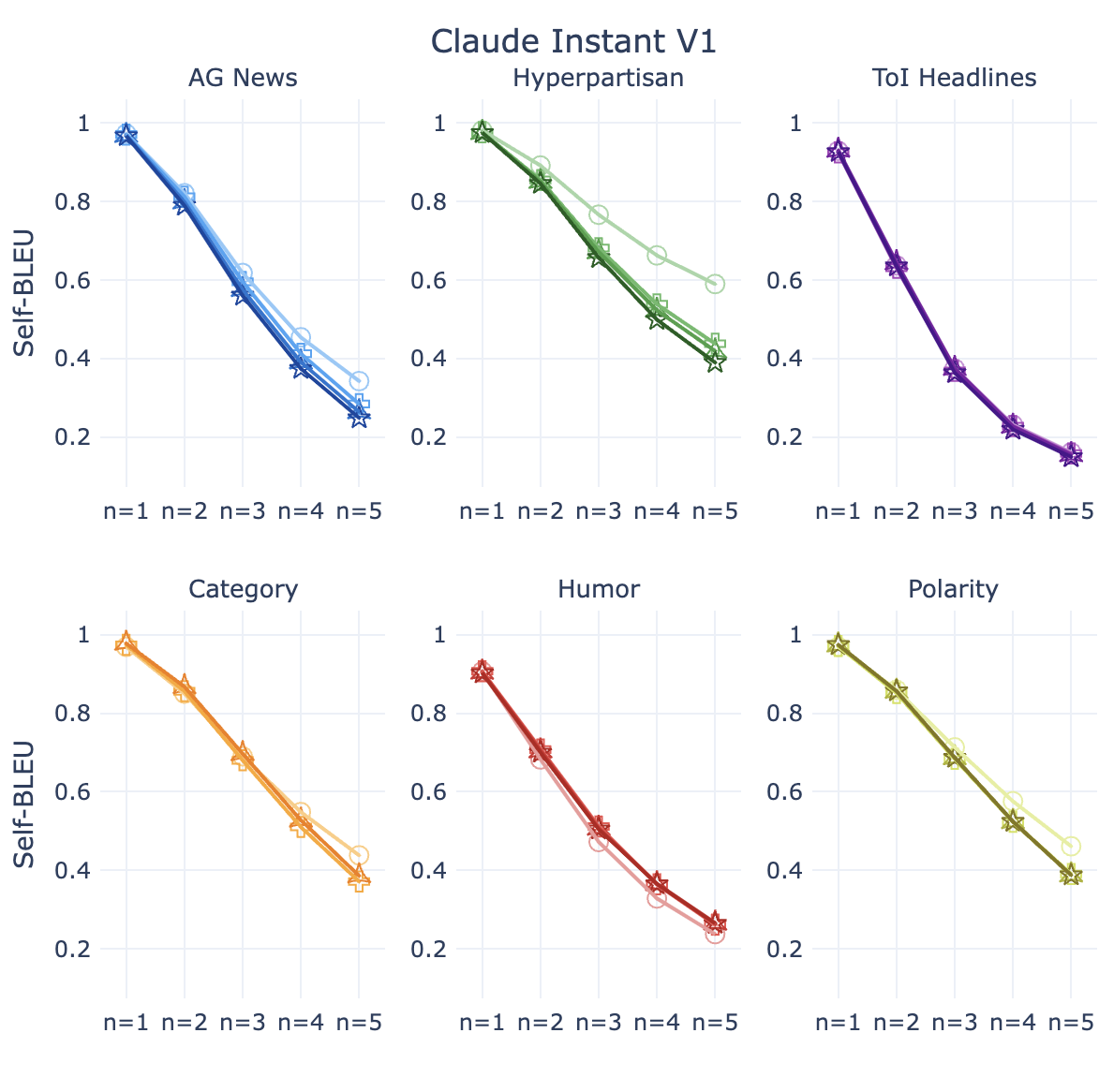
RQ:检索增强是否可以提高词汇多样性? Figure 3 显示了数据集中的词汇多样性。 人类编写的文本 (Gold) 在词汇多样性方面得分较高(Self-BLEU 较低)。 FewGen 文本倾向于重复使用相同的单词和短语,导致跨代重复文本(高 Self-BLEU)。 对于所有 n 元语法值,SynthesizRR 文本的词汇多样性接近人类文本。 我们注意到情境学习的效果不一致;它提高了新闻语料库的词汇多样性,但没有提高产品的词汇多样性。
RQ:SynthesizRR 是否解决了实体多样性问题? 流行度偏差是大语言模型世代倾向于过度代表流行“头部”实体的现象。 这已针对 QA 任务进行了研究(Mallen 等人,2023;Kandpal 等人,2023)。
在Figure 4 中,我们看到 SynthesizRR 如何消除实体类型之间的流行度偏差。 通过从检索结果的长尾 () 中获取,生成的数据集与 FewGen 相比具有更高的实体熵。 这使得 SynthesizRR 更接近 Gold,这也显示出较高的实体熵。
| Method | AG. | Hyp. | ToI | Cat. | Hum. | Pol. |
| (Dataset size) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) |
| Zero shot | ||||||
| FewGen | 63.2 | |||||
| SynzthRR | 90.3 | 59.2 | 63.0 | 82.9 | 78.6 | |
| Few shot | ||||||
| FewGen* | ||||||
| SynzthRR† | 92.0 | 72.8 | 87.9 | 75.2 | 87.5 | 89.9 |
| SynzthRR‡ | ||||||
| Method | Teacher LM | AG. | Hyper. | ToI | Categ. | Humor | Polar. | Avg | |
| (Dataset size) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | |||
| Gold | 89.43 | ||||||||
| Zero shot | |||||||||
| FewGen | LLaMa2 | 72.6 | 65.32 | ||||||
| FewGen | ClaudeV1 | 56.72 | |||||||
| SynthesizRR | LLaMa2 | 74.4 | 68.9 | 82.5 | 77.32 | ||||
| SynthesizRR | ClaudeV1 | 83.9 | 88.7 | 74.29 | |||||
| Few shot | |||||||||
| FewGen* | LLaMa2 | 73.7 | 80.05 | ||||||
| FewGen* | ClaudeV1 | 74.93 | |||||||
| SynthesizRR† | LLaMa2 | 72.4 | 90.2 | 81.38 | |||||
| SynthesizRR‡ | LLaMa2 | 85.2 | 79.1 | 81.00 | |||||
| SynthesizRR† | ClaudeV1 | 91.3 | 78.16 | ||||||
| SynthesizRR‡ | ClaudeV1 | 76.68 | |||||||
RQ:基于域内语料库如何影响合成数据中的实体相似性? 对于类别任务,我们生成K个产品评论并随机选择K个金牌个示例。 在Table 4中,我们测量了实体召回率,发现Gold实体的出现率在SynthesizRR中高出100%-140% 高于 FewGen。 每个实体分布的KL散度也较低。 我们最后考虑实体覆盖(唯一实体)和实体密度(总实体)。 与黄金相比,FewGen往往会产生较少的独特实体(地点、事件、语言、货币等)。 每个 FewGen 示例还具有较低的实体密度,如Table 3 中所示。 SynthesizRR 覆盖范围和密度更接近Gold。
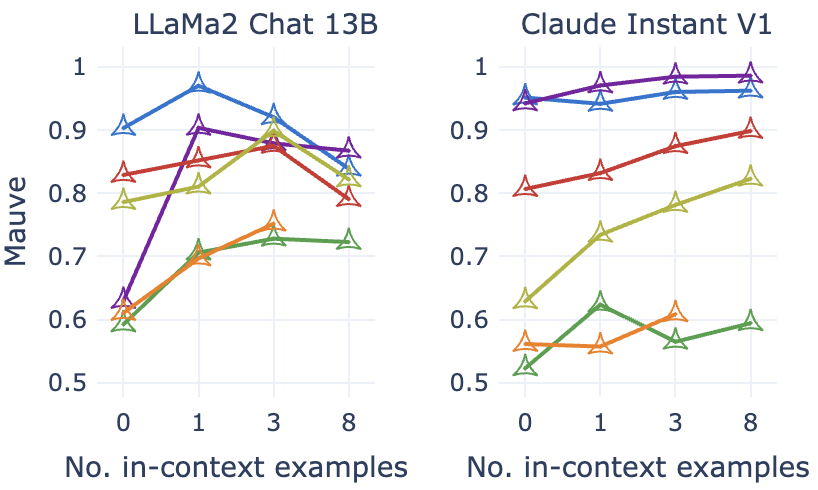
RQ:我们生成的示例和人工编写的示例在分布上有多相似? 从Table 5中的MAUVE分数我们可以看出,与少样本方法相比,两种方法的零样本生成非常不同。
令人惊讶的是,SynthesizRR 代比 FewGen 更类似于人类文本,尽管我们的内容采购策略中没有任何内容明确指导 SynthesizRR 代匹配Gold的分布。 因此,我们手动检查各代并发现一个有趣的模式,该模式可归因于内容采购。 如前所述,在Table 3 中,SynthesizRR 下实体的密度更高。 FewGen 生成的生成遵循提示,但非常平淡且不包含细节。 另一方面,通过获取信息丰富的文档,SynthesizRR能够将任务反转步骤基于检索到的文章/产品的细节。 我们假设这会将 MAUVE 得分提高到 Gold,这同样基于细节。
6 结果:学生蒸馏
我们已经确定,与基线方法相比,SynthesizRR 生成的数据集更加多样化。 现在,我们回到基于这些数据集训练专家模型的应用。
Table 6 显示了 DeBERTa-v3-Large 学生在 SynthesizRR 和 FewGen 生成的数据集上训练的结果。 在零样本设置中,我们发现SynthesizRR的表现比FewGen好得多,尽管使用相同的冻结教师大语言模型。 请注意,SynthesizRR 使用上下文示例进行检索,而 FewGen 则不使用;我们的方法在这里有一些额外的监督。 然而,在这种情况下,我们在任务反转阶段看到了明显的收益(对于 LLaMa 为 12%,对于 Claude< 为 17.6%) /t3>)。 因此,访问检索会产生更好的最终数据集,几乎与 32 镜头 FewGen 相当。
借助 ICL,使用 RetrICL 策略的 3 次 SynthesizRR 比 32 次 FewGen 训练的学生效果更好 (1.3%对于LLaMa和对于Claude为3.2%)和Non-RetrICL。 我们得出的结论是,天真地添加 ICL 示例并不能有效地利用大语言模型的上下文窗口。 相反,更好的内容采购策略可以改善学生的精炼,从而提高测试成绩。
7 结果:与之前的工作比较
| Method | LM | MAUVE | Accuracy | |||||||
| (Dataset) | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | ||||
| Gold | - | - | - | - | 90.8 | 91.3 | 88.2 | |||
| SunGen | gpt2-xl |
|
68.7 |
|
|
84.9 |
|
|||
| ReGen | BERT | 68.1 |
|
|
82.7 |
|
|
|||
| S3 | gpt3.5 |
|
62.0 |
|
|
87.1 |
|
|||
| AttPmt | gpt3.5-t | 52.8 |
|
50.0 | 79.8 |
|
80.8 | |||
| Zero shot | ||||||||||
| (Ours) | LLaMa | 89.5 | 58.5 | 50.0 | 85.3 | 82.9 | 80.2 | |||
| (Ours) | Claude | 94.2 | 55.9 | 50.0 | 85.6 | 83.6 | 82.5 | |||
| 3-shot RetrICL | ||||||||||
| (Ours) | LLaMa | 92.6 | 72.6 | 50.0 | 84.6 | 84.8 | 83.8 | |||
| (Ours) | Claude | 95.8 | 58.0 | 50.0 | 86.0 | 86.3 | 80.6 | |||
我们将 SynthesizRR 与四种有竞争力的先前方法进行比较:SunGen (Gao 等人,2023)、ReGen (于等人, 2023b), S3 (王等人, 2023a) 和 AttrPrompt 于等人 ( 2023a)。 Table 7 评估了与人类文本的整体相似性和蒸馏准确性,完整的详细信息参见Appendix B。
我们观察到 SynthesizRR 优于生成高多样性协变量 (AttrPrompt) 或使用内容源 (ReGen) 的方法。 即使使用固定的学生模型,它也比利用学生反馈的方法 (SunGen) 提高了准确性,并且在Appendix C 中,我们看到学生反馈可以进一步提高准确性。 像 S3 这样使用迭代提示和思想链推理的方法(Wei等人,2022)可以提供较小的准确性改进,但世代不太现实。 我们最终观察到仅使用检索的 ReGen 在词汇多样性和学生准确性方面受到影响;任务反转对于转换检索到的上下文以匹配人类编写的协变量是必要的。
我们强调情感和主题分类是简单的综合任务。 我们将它们包括在内是为了与之前的工作进行比较,但相信我们在更具挑战性的任务上的实验更好地代表了大语言模型数据集综合的能力。
8相关工作
使用大语言模型进行数据集合成。 之前已经研究过使用大语言模型执行任务反演来进行数据集综合。 大多数使用 GPT-2XL 而不进行微调(Ye 等人,2022b,a;Gao 等人,2023;Meng 等人,2022;Schick 和 Schütze,2021;Jung 等人,2023)。 最近的工作考虑了大型教师大语言模型,例如 GPT-3 (West 等人, 2022; Honovich 等人, 2023; Wang 等人, 2023b)、PaLM-540B (Hsieh 等人, 2023) 以及聊天调优的大语言模型,例如 gpt-3.5-turbo (Yu 等人, 2023a; Yehudai 等人, 2024b; Wang 等人, 2023a )。
对于文本分类数据集的生成,类条件提示是关键。 先前的方法研究零样本(Ye等人,2022a)和迭代少样本提示(Ye等人,2022b),或使用seq2seq大语言模型进行微调的合成精选数据集(Lee 等人,2021)。 最近,AttrPrompt (Yu 等人,2023a) 证实不同的提示属性可以提高多样性。 我们的工作探索添加检索上下文作为多样性的来源。
检索增强一代。 我们的方法具有上下文检索增强生成(RAG)的许多特征(Lewis 等人,2020;Ram 等人,2023;Huang 等人,2023;Izacard 等人,2023) 。 之前的研究表明,RAG 如何绕过与仅从参数记忆生成相关的众多问题,即对“头部”实体的偏向加剧(Mallen 等人,2023)、较低的词汇多样性(Holtzman 等人) ,2019;Jentzsch 和 Kersting,2023),以及幻觉信息(张等人,2023)。
尚未在实例级别探索使用检索增强生成来综合分类任务。 ReGen (Yu 等人, 2023b) 研究了用于创建主题和情感数据集的仅检索设置,这比我们工作中的任务更简单。 Viswanathan 等人 (2023) 和 Gandhi 等人 (2024) 执行数据集级检索,而不是实例级检索。
数据集合成的多样性。 RAG 和 SynthesizRR 之间的一个重要区别是对不同世代的渴望。 迄今为止,RAG 主要用于基于知识的任务,例如开放域问答、事实检查和少样本分类(Asai 等人,2023)。 这些任务面临多个有效表面形式的问题,这些表面形式只会改变生成输出的措辞,但不会改变其含义,使得评估变得困难(Holtzman等人,2021)。 贪婪采样是最常用的。
另一方面,数据集合成受到不同表面形式的鼓励,因为这会产生与同一目标相关的不同协变量,这直观地有助于泛化;因此,我们使用 top-p 采样(Holtzman 等人, 2019)。 与 RAG 的另一个主要区别是我们保留了检索结果的长尾,因为这使我们能够创建多样化的基础数据集。
9结论
在这项工作中,我们描述了如何使用检索语料库来帮助合成专门领域中的文本分类数据集。 我们表明,通过在生成提示中包含检索到的文档,可以增强生成数据的多样性。 与少样本生成相比,我们发现 SynthesizRR 生成更加多样化和代表性的文本,并培养出更好的学生。
局限性
最重要的是,我们的工作依赖于足够接近手头任务的大型语料库的存在。 这对于以低资源语言进行数据集生成可能是禁止的,因为在低资源语言中可能无法获得大量相关内容的语料库。 探索内容来源的跨语言传输将会很有趣,但这需要额外的实验验证。 相比之下,像 FewGen 这样的方法不需要这个语料库。
对显式上下文源步骤和增加提示长度的需求会导致费用和延迟的增加,特别是在使用大语言模型 API 时。 在检索语料库质量较差的情况下,这种增加的费用可能不值得。 其一,如果上下文示例不易作为查询重用,则 SynthesizRR 可以检索可能不适合任务反转的不相关文档。 此外,在事实可疑的语料库文档的情况下,学生模型最终可能会基于事实不正确的信息。 这可以通过在任务反转之前删除此类文档的人机交互步骤来缓解。
最后,我们注意到我们的实验范围仅限于几个英语文本域的一组分类任务。 虽然我们相信我们的方法可以应用于其他语言、其他领域以及超越分类的问答等任务,但我们尚未在这项工作中验证这一点。
参考
- Anthropic (2023) Anthropic. 2023. Claude v1.2 instant. https://www.anthropic.com/news/releasing-claude-instant-1-2.
- Asai et al. (2023) Akari Asai, Sewon Min, Zexuan Zhong, and Danqi Chen. 2023. Retrieval-based language models and applications. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 6: Tutorial Abstracts), pages 41–46, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Bai et al. (2022) Yuntao Bai, Andy Jones, Kamal Ndousse, Amanda Askell, Anna Chen, Nova DasSarma, Dawn Drain, Stanislav Fort, Deep Ganguli, T. J. Henighan, Nicholas Joseph, Saurav Kadavath, John Kernion, Tom Conerly, Sheer El-Showk, Nelson Elhage, Zac Hatfield-Dodds, Danny Hernandez, Tristan Hume, Scott Johnston, Shauna Kravec, Liane Lovitt, Neel Nanda, Catherine Olsson, Dario Amodei, Tom B. Brown, Jack Clark, Sam McCandlish, Christopher Olah, Benjamin Mann, and Jared Kaplan. 2022. Training a helpful and harmless assistant with reinforcement learning from human feedback. ArXiv, abs/2204.05862.
- Bamman et al. (2013) David Bamman, Brendan O’Connor, and Noah A. Smith. 2013. Learning latent personas of film characters. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 352–361, Sofia, Bulgaria. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Borisov et al. (2022) Vadim Borisov, Kathrin Sessler, Tobias Leemann, Martin Pawelczyk, and Gjergji Kasneci. 2022. Language models are realistic tabular data generators. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Brown et al. (2020) Tom Brown, Benjamin Mann, Nick Ryder, Melanie Subbiah, Jared D Kaplan, Prafulla Dhariwal, Arvind Neelakantan, Pranav Shyam, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Sandhini Agarwal, Ariel Herbert-Voss, Gretchen Krueger, Tom Henighan, Rewon Child, Aditya Ramesh, Daniel Ziegler, Jeffrey Wu, Clemens Winter, Chris Hesse, Mark Chen, Eric Sigler, Mateusz Litwin, Scott Gray, Benjamin Chess, Jack Clark, Christopher Berner, Sam McCandlish, Alec Radford, Ilya Sutskever, and Dario Amodei. 2020. Language models are few-shot learners. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 33, pages 1877–1901. Curran Associates, Inc.
- Bubeck et al. (2023) Sébastien Bubeck, Varun Chandrasekaran, Ronen Eldan, Johannes Gehrke, Eric Horvitz, Ece Kamar, Peter Lee, Yin Tat Lee, Yuanzhi Li, Scott Lundberg, et al. 2023. Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2303.
- Chang et al. (2024) Yupeng Chang, Xu Wang, Jindong Wang, Yuan Wu, Linyi Yang, Kaijie Zhu, Hao Chen, Xiaoyuan Yi, Cunxiang Wang, Yidong Wang, Wei Ye, Yue Zhang, Yi Chang, Philip S. Yu, Qiang Yang, and Xing Xie. 2024. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol.
- Chen et al. (2017) Danqi Chen, Adam Fisch, Jason Weston, and Antoine Bordes. 2017. Reading Wikipedia to answer open-domain questions. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 1870–1879, Vancouver, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Devlin et al. (2019) Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova. 2019. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long and Short Papers), pages 4171–4186, Minneapolis, Minnesota. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Gandhi et al. (2024) Saumya Gandhi, Ritu Gala, Vijay Viswanathan, Tongshuang Wu, and Graham Neubig. 2024. Better synthetic data by retrieving and transforming existing datasets.
- Gao et al. (2023) Jiahui Gao, Renjie Pi, LIN Yong, Hang Xu, Jiacheng Ye, Zhiyong Wu, Weizhong Zhang, Xiaodan Liang, Zhenguo Li, and Lingpeng Kong. 2023. Self-guided noise-free data generation for efficient zero-shot learning. In The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Goyal et al. (2022) Tanya Goyal, Junyi Jessy Li, and Greg Durrett. 2022. News Summarization and Evaluation in the Era of GPT-3. arXiv preprint.
- He et al. (2021) Pengcheng He, Jianfeng Gao, and Weizhu Chen. 2021. DeBERTaV3: Improving DeBERTa using ELECTRA-Style Pre-Training with Gradient-Disentangled Embedding Sharing.
- Holtzman et al. (2019) Ari Holtzman, Jan Buys, Li Du, Maxwell Forbes, and Yejin Choi. 2019. The curious case of neural text degeneration. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Holtzman et al. (2021) Ari Holtzman, Peter West, Vered Shwartz, Yejin Choi, and Luke Zettlemoyer. 2021. Surface form competition: Why the highest probability answer isn’t always right. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 7038–7051, Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Honnibal et al. (2020) Matthew Honnibal, Ines Montani, Sofie Van Landeghem, and Adriane Boyd. 2020. spaCy: Industrial-strength Natural Language Processing in Python.
- Honovich et al. (2023) Or Honovich, Thomas Scialom, Omer Levy, and Timo Schick. 2023. Unnatural instructions: Tuning language models with (almost) no human labor. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 14409–14428, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Hsieh et al. (2023) Cheng-Yu Hsieh, Chun-Liang Li, Chih-kuan Yeh, Hootan Nakhost, Yasuhisa Fujii, Alex Ratner, Ranjay Krishna, Chen-Yu Lee, and Tomas Pfister. 2023. Distilling step-by-step! outperforming larger language models with less training data and smaller model sizes. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023, pages 8003–8017, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Huang et al. (2023) Jie Huang, Wei Ping, Peng Xu, Mohammad Shoeybi, Kevin Chen-Chuan Chang, and Bryan Catanzaro. 2023. Raven: In-context learning with retrieval augmented encoder-decoder language models. ArXiv, abs/2308.07922.
- Izacard et al. (2022) Gautier Izacard, Mathilde Caron, Lucas Hosseini, Sebastian Riedel, Piotr Bojanowski, Armand Joulin, and Edouard Grave. 2022. Unsupervised dense information retrieval with contrastive learning. Transactions on Machine Learning Research.
- Izacard et al. (2023) Gautier Izacard, Patrick Lewis, Maria Lomeli, Lucas Hosseini, Fabio Petroni, Timo Schick, Jane Dwivedi-Yu, Armand Joulin, Sebastian Riedel, and Edouard Grave. 2023. Atlas: Few-shot learning with retrieval augmented language models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 24(251):1–43.
- Jentzsch and Kersting (2023) Sophie Jentzsch and Kristian Kersting. 2023. ChatGPT is fun, but it is not funny! humor is still challenging large language models. In Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity, Sentiment, & Social Media Analysis, pages 325–340, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Jung et al. (2023) Jaehun Jung, Peter West, Liwei Jiang, Faeze Brahman, Ximing Lu, Jillian Fisher, Taylor Sorensen, and Yejin Choi. 2023. Impossible distillation: from low-quality model to high-quality dataset & model for summarization and paraphrasing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.16635.
- Kandpal et al. (2023) Nikhil Kandpal, Haikang Deng, Adam Roberts, Eric Wallace, and Colin Raffel. 2023. Large language models struggle to learn long-tail knowledge. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML’23. JMLR.org.
- Kiesel et al. (2019) Johannes Kiesel, Maria Mestre, Rishabh Shukla, Emmanuel Vincent, Payam Adineh, David Corney, Benno Stein, and Martin Potthast. 2019. SemEval-2019 task 4: Hyperpartisan news detection. In Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, pages 829–839, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Kingma and Ba (2015) Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. 2015. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, May 7-9, 2015, Conference Track Proceedings.
- Lee et al. (2023) Harrison Lee, Samrat Phatale, Hassan Mansoor, Thomas Mesnard, Johan Ferret, Kellie Lu, Colton Bishop, Ethan Hall, Victor Carbune, Abhinav Rastogi, and Sushant Prakash. 2023. RLAIF: Scaling Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback with AI Feedback.
- Lee et al. (2019) Kenton Lee, Ming-Wei Chang, and Kristina Toutanova. 2019. Latent retrieval for weakly supervised open domain question answering. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, pages 6086–6096, Florence, Italy. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Lee et al. (2021) Kenton Lee, Kelvin Guu, Luheng He, Timothy Dozat, and Hyung Won Chung. 2021. Neural data augmentation via example extrapolation. ArXiv, abs/2102.01335.
- Lewis et al. (2020) Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandra Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, and Douwe Kiela. 2020. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
- Liu et al. (2021) Lang Liu, Krishna Pillutla, Sean Welleck, Sewoong Oh, Yejin Choi, and Zaid Harchaoui. 2021. Divergence Frontiers for Generative Models: Sample Complexity, Quantization Effects, and Frontier Integrals. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
- Liu et al. (2023) Nelson F. Liu, Kevin Lin, John Hewitt, Ashwin Paranjape, Michele Bevilacqua, Fabio Petroni, and Percy Liang. 2023. Lost in the middle: How language models use long contexts. ArXiv:2307.03172.
- Maas et al. (2011) Andrew L. Maas, Raymond E. Daly, Peter T. Pham, Dan Huang, Andrew Y. Ng, and Christopher Potts. 2011. Learning word vectors for sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 142–150, Portland, Oregon, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Mallen et al. (2023) Alex Mallen, Akari Asai, Victor Zhong, Rajarshi Das, Daniel Khashabi, and Hannaneh Hajishirzi. 2023. When not to trust language models: Investigating effectiveness of parametric and non-parametric memories. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 9802–9822, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Meng et al. (2022) Yu Meng, Jiaxin Huang, Yu Zhang, and Jiawei Han. 2022. Generating training data with language models: Towards zero-shot language understanding. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35:462–477.
- Mialon et al. (2023) Grégoire Mialon, Roberto Dessi, Maria Lomeli, Christoforos Nalmpantis, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Roberta Raileanu, Baptiste Roziere, Timo Schick, Jane Dwivedi-Yu, Asli Celikyilmaz, Edouard Grave, Yann LeCun, and Thomas Scialom. 2023. Augmented language models: a survey. Transactions on Machine Learning Research. Survey Certification.
- Ni et al. (2019) Jianmo Ni, Jiacheng Li, and Julian McAuley. 2019. Justifying recommendations using distantly-labeled reviews and fine-grained aspects. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pages 188–197, Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- OpenAI (2022) OpenAI. 2022. Gpt-3.5 (text-davinci-003). https://platform.openai.com/docs/models/gpt-3-5-turbo.
- OpenAI (2023) OpenAI. 2023. GPT-4 Technical Report.
- Ouyang et al. (2022) Long Ouyang, Jeff Wu, Xu Jiang, Diogo Almeida, Carroll L. Wainwright, Pamela Mishkin, Chong Zhang, Sandhini Agarwal, Katarina Slama, Alex Ray, John Schulman, Jacob Hilton, Fraser Kelton, Luke Miller, Maddie Simens, Amanda Askell, Peter Welinder, Paul Christiano, Jan Leike, and Ryan Lowe. 2022. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
- Papineni et al. (2002) Kishore Papineni, Salim Roukos, Todd Ward, and Wei-Jing Zhu. 2002. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL ’02, page 311–318, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Radford et al. (2019) Alec Radford, Jeff Wu, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei, and Ilya Sutskever. 2019. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners.
- Ram et al. (2023) Ori Ram, Yoav Levine, Itay Dalmedigos, Dor Muhlgay, Amnon Shashua, Kevin Leyton-Brown, and Yoav Shoham. 2023. In-context retrieval-augmented language models. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 11:1316–1331.
- Robertson and Zaragoza (2009) Stephen Robertson and Hugo Zaragoza. 2009. The probabilistic relevance framework: Bm25 and beyond. Found. Trends Inf. Retr., 3(4):333–389.
- Sanh et al. (2019) Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut, Julien Chaumond, and Thomas Wolf. 2019. DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. In 5th Workshop on Energy Efficient Machine Learning and Cognitive Computing @ NeurIPS 2019.
- Schick and Schütze (2021) Timo Schick and Hinrich Schütze. 2021. Generating datasets with pretrained language models. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 6943–6951, Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Socher et al. (2013) Richard Socher, Alex Perelygin, Jean Wu, Jason Chuang, Christopher D. Manning, Andrew Ng, and Christopher Potts. 2013. Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 1631–1642, Seattle, Washington, USA. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Swayamdipta et al. (2020) Swabha Swayamdipta, Roy Schwartz, Nicholas Lourie, Yizhong Wang, Hannaneh Hajishirzi, Noah A. Smith, and Yejin Choi. 2020. Dataset cartography: Mapping and diagnosing datasets with training dynamics. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 9275–9293, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Touvron et al. (2023a) Hugo Touvron, Thibaut Lavril, Gautier Izacard, Xavier Martinet, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Timothée Lacroix, Baptiste Rozière, Naman Goyal, Eric Hambro, Faisal Azhar, et al. 2023a. Llama: Open and efficient foundation language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.13971.
- Touvron et al. (2023b) Hugo Touvron, Louis Martin, Kevin Stone, Peter Albert, Amjad Almahairi, Yasmine Babaei, Nikolay Bashlykov, Soumya Batra, Prajjwal Bhargava, Shruti Bhosale, et al. 2023b. Llama 2: Open foundation and fine-tuned chat models. arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv–2307.
- van de Kar et al. (2022) Mozes van de Kar, Mengzhou Xia, Danqi Chen, and Mikel Artetxe. 2022. Don’t prompt, search! mining-based zero-shot learning with language models. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 7508–7520, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Viswanathan et al. (2023) Vijay Viswanathan, Chenyang Zhao, Amanda Bertsch, Tongshuang Wu, and Graham Neubig. 2023. Prompt2Model: Generating deployable models from natural language instructions. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, pages 413–421, Singapore. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Wang et al. (2023a) Ruida Wang, Wangchunshu Zhou, and Mrinmaya Sachan. 2023a. Let’s synthesize step by step: Iterative dataset synthesis with large language models by extrapolating errors from small models. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, pages 11817–11831, Singapore. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Wang et al. (2023b) Yizhong Wang, Yeganeh Kordi, Swaroop Mishra, Alisa Liu, Noah A. Smith, Daniel Khashabi, and Hannaneh Hajishirzi. 2023b. Self-instruct: Aligning language models with self-generated instructions. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 13484–13508, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Wei et al. (2022) Jason Wei, Xuezhi Wang, Dale Schuurmans, Maarten Bosma, brian ichter, Fei Xia, Ed H. Chi, Quoc V Le, and Denny Zhou. 2022. Chain of thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.
- West et al. (2022) Peter West, Chandra Bhagavatula, Jack Hessel, Jena Hwang, Liwei Jiang, Ronan Le Bras, Ximing Lu, Sean Welleck, and Yejin Choi. 2022. Symbolic knowledge distillation: from general language models to commonsense models. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 4602–4625, Seattle, United States. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Ye et al. (2022a) Jiacheng Ye, Jiahui Gao, Qintong Li, Hang Xu, Jiangtao Feng, Zhiyong Wu, Tao Yu, and Lingpeng Kong. 2022a. Zerogen: Efficient zero-shot learning via dataset generation. ArXiv, abs/2202.07922.
- Ye et al. (2022b) Jiacheng Ye, Jiahui Gao, Zhiyong Wu, Jiangtao Feng, Tao Yu, and Lingpeng Kong. 2022b. ProGen: Progressive zero-shot dataset generation via in-context feedback. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2022, pages 3671–3683, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Yehudai et al. (2024a) Asaf Yehudai, Boaz Carmeli, Yosi Mass, Ofir Arviv, Nathaniel Mills, Assaf Toledo, Eyal Shnarch, and Leshem Choshen. 2024a. Achieving human parity in content-grounded datasets generation. In International Conference on Learning Representations.
- Yehudai et al. (2024b) Asaf Yehudai, Boaz Carmeli, Yosi Mass, Ofir Arviv, Nathaniel Mills, Assaf Toledo, Eyal Shnarch, and Leshem Choshen. 2024b. Genie: Achieving human parity in content-grounded datasets generation. ArXiv, abs/2401.14367.
- Yu et al. (2023a) Yue Yu, Yuchen Zhuang, Jieyu Zhang, Yu Meng, Alexander Ratner, Ranjay Krishna, Jiaming Shen, and Chao Zhang. 2023a. Large language model as attributed training data generator: A tale of diversity and bias. In Thirty-seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track.
- Yu et al. (2023b) Yue Yu, Yuchen Zhuang, Rongzhi Zhang, Yu Meng, Jiaming Shen, and Chao Zhang. 2023b. ReGen: Zero-shot text classification via training data generation with progressive dense retrieval. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023, pages 11782–11805, Toronto, Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
- Zellers et al. (2019) Rowan Zellers, Ari Holtzman, Hannah Rashkin, Yonatan Bisk, Ali Farhadi, Franziska Roesner, and Yejin Choi. 2019. Defending against neural fake news. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32.
- Zhang et al. (2015) Xiang Zhang, Junbo Zhao, and Yann LeCun. 2015. Character-level convolutional networks for text classification. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1, NIPS’15, page 649–657, Cambridge, MA, USA. MIT Press.
- Zhang et al. (2023) Yue Zhang, Yafu Li, Leyang Cui, Deng Cai, Lemao Liu, Tingchen Fu, Xinting Huang, Enbo Zhao, Yu Zhang, Yulong Chen, Longyue Wang, Anh Tuan Luu, Wei Bi, Freda Shi, and Shuming Shi. 2023. Siren’s song in the ai ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.01219.
- Zhu et al. (2018) Yaoming Zhu, Sidi Lu, Lei Zheng, Jiaxian Guo, Weinan Zhang, Jun Wang, and Yong Yu. 2018. Texygen: A benchmarking platform for text generation models. SIGIR.
- Ziser et al. (2020) Yftah Ziser, Elad Kravi, and David Carmel. 2020. Humor detection in product question answering systems. In Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, SIGIR ’20, page 519–528, New York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
附录A风险
尽管我们工作的主要目标是改进文本分类,但我们使用大语言模型来生成示例确实存在一些概念风险。 通过生成新闻文章来训练分类器,我们面临着生成假新闻和其他有害内容的风险。 然而,我们认为,我们系统的最终结果是一个分类器,这一事实减轻了这种风险:与可能误导用户的文本生成模型相比,分类模型具有相对受限的故障模式(错误分类)。 此外,我们不相信我们的方法能够独特地促进假新闻等内容的生成;我们的进步在很大程度上与带来此类风险的技术是正交的。
附录B与之前工作的详细比较
| Method | Retriever | Teacher | Self-BLEU-5 | Entity Entropy | Mauve | Accuracy | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Dataset) | LLM | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | AG. | IMDb | SST-2 | |||||
| Gold | - | - | 17.1 | 27.9 | 35.5 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 3.2 | - | - | - | 90.8 | 91.3 | 88.2 | ||||
| SunGen | - | GPT2-XL |
|
15.4 |
|
|
4.9 |
|
|
68.7 |
|
|
84.9 |
|
||||
| ReGen | BERT | - | 56.5 |
|
|
8.1 |
|
|
68.1 |
|
|
82.7 |
|
|
||||
| S3 | - | GPT3.5 |
|
62.2 |
|
|
5.7 |
|
|
62.0 |
|
|
87.1 |
|
||||
| AttPmt | - | GPT3.5-T | 39.8 |
|
71.5 | 6.0 |
|
3.4 | 52.8 |
|
50.0 | 79.8 |
|
80.8 | ||||
| Zero shot | ||||||||||||||||||
| SynzthRR | Contr. | LLaMa2 | 29.3 | 66.3 | 41.9 | 7.1 | 5.7 | 4.5 | 89.5 | 58.5 | 50.0 | 85.3 | 82.9 | 80.2 | ||||
| SynzthRR | Contr. | ClaudeV1 | 31.5 | 51.5 | 45.3 | 6.6 | 5.3 | 4.8 | 94.2 | 55.9 | 50.0 | 85.6 | 83.6 | 82.5 | ||||
| SynzthRR | BM25 | LLaMa2 | 28.7 | 62.2 | 36.5 | 7.0 | 5.6 | 5.1 | 90.3 | 60.5 | 50.0 | 84.3 | 74.1 | 84.4 | ||||
| SynzthRR | BM25 | ClaudeV1 | 30.9 | 50.4 | 36.9 | 6.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 90.8 | 53.2 | 50.0 | 84.2 | 79.1 | 82.6 | ||||
| 3-shot RetrICL | ||||||||||||||||||
| SynzthRR | Contr. | LLaMa2 | 34.2 | 62.9 | 26.3 | 7.2 | 5.7 | 3.8 | 92.6 | 72.6 | 50.0 | 84.6 | 84.8 | 83.8 | ||||
| SynzthRR | Contr. | ClaudeV1 | 23.7 | 38.0 | 24.6 | 6.7 | 5.9 | 4.3 | 95.8 | 58.0 | 50.0 | 86.0 | 86.3 | 80.6 | ||||
| SynzthRR | BM25 | LLaMa2 | 32.0 | 59.7 | 25.3 | 7.2 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 92.5 | 78.7 | 50.0 | 84.3 | 84.7 | 84.4 | ||||
| SynzthRR | BM25 | ClaudeV1 | 24.6 | 41.9 | 26.8 | 6.7 | 5.4 | 4.9 | 96.0 | 58.5 | 50.0 | 84.1 | 81.6 | 82.3 | ||||
在这里,我们探讨 SynthesizRR 如何直接与之前流行数据集综合的工作进行比较。 我们与四种先前的方法进行比较:
孙根 高等人 (2023): 使用 ZeroGen 策略生成大型综合数据集(200k 行)。 然后,使用自定义双层优化算法(涉及学生模型)来确定每个合成示例的实例权重。
再生 于等人 (2023b): 使用 2 个 BERT 模型对检索结果进行多轮过滤;一个训练用于检索,一个分类器。 使用这些模型之间的一致性来过滤噪声数据。
S3 王等人 (2023a): 构建“种子数据集”(与我们的不同)并训练学生模型。 然后,使用大语言模型推断错误并综合附加数据。 我们将其与种子数据结合起来并重复该过程。
属性提示符 于等人 (2023a): 一种专注于提高生成数据集的多样性和公正性的方法。 作者提出了一个强大的大语言模型,如GPT3.5-Turbo,具有不同的属性,每个属性都具有不同的维度。 使用 GPT3.5-Turbo 从任务的人机交互分析中提取属性。
标准零样本和少样本生成基线在Table 6中进行了比较,因此我们在此不包括它们。222ZeroGen (Ye 等人, 2022a) 同样不予考虑。
我们对先前工作中流行的三个分类任务进行了基准测试:IMDb Maas 等人 (2011)、SST-2 Socher 等人(2013) 和 AG News (张等人,2015)。 前两个任务是电影评论的二元情感分析,而后者是新闻的多类主题分类。
之前的工作生成了更大的数据集(20k 到 200k 示例)并使用不同的学生模型超参数。 数据集质量的内在评估也很少被报道。 这使得公平比较结果变得困难。 因此,我们通过使用作者发布的合成数据集来重现结果。333ProGen (Ye 等人, 2022b) 是相关技术,但不发布数据集。 遵循 Yu 等人 (2023a),我们将这些数据集二次采样为 6,000 行,保持跨类的均匀分布,并使用 SynthesizRR RetrICL 生成相同数量的合成协变量(算法1)。 对于SynthesizRR的内容采购阶段,我们从以下语料库中检索文档:
-
•
电影:为IMDb和SST-2生成电影评论,我们从CMU电影检索摘要语料库Bamman等人(2013),包含42k条情节摘要。
-
•
RealNews/Dom:对于AG News,我们使用Table 2中的RealNews/Dominant ,其中包含来自美国、欧盟国家、英国和澳大利亚的 3000 万篇新闻文章,这是 RealNews 的“主导”部分(完整详细信息请参阅Appendix J)。
DistilBERT (Sanh 等人, 2019) 在之前的工作中被广泛使用 Yu 等人 (2023a);叶等人 (2022a);高等人 (2023);王等人 (2023a); Ye 等人 (2022b),因此我们用它作为学生模型来衡量准确性。 我们使用与 Yu 等人 (2023a) 相同的训练超参数,即 Adam optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2015) 使用 lr=2e-5 、 batch_size=32 、 weight_decay=1e-4 和 epsilon=1e-6 ,以及6% 训练步骤的线性学习率预热。
RQ:在提取学生准确性方面,SynthesizRR 与现有方法相比如何?
像SunGen这样的方法依赖于相对较弱的大语言模型教师,例如GPT2-XLRadford等人(2019)可以在主题和情感上表现良好类似于 IMDb 的任务,但需要非常高的数据成本(合成数据比 SynthesizRR 多 15-30 倍)。 在Table 8中,我们观察到当缩小到6k行时,性能显着恶化。
使用强指令遵循的大语言模型(如 AttrPrompt、S3 和 SynthesizRR)的方法可以使用更小的数据集实现类似或更好的性能。 这些方法创建高质量的数据集,而不是像 SunGen 和 ProGen 那样修改学生建模过程。 SunGen 对 ZeroGen 数据集执行迭代双层优化,共同学习实例权重并改进学生。 我们假设在综合过程中添加学生模型也会影响最终的分类准确性,因为数据集变得专门针对学生及其超参数的特定选择。 在此处的标准学生蒸馏设置下,这些方法的数据集可能表现不佳。
S3 使用的更复杂的提示技术,例如 Chain-of-Thought (Wei 等人, 2022) 确实可以改进任务反转步骤,尽管这需要更高的 API 成本由于输出长度较长。 因此,思想链提示似乎是增强 SynthesizRR 任务反转步骤的一种有前途的方法。
RQ:我们是否找到证据表明内容采购可以促进多样性和相似性?
在Table 8中,我们与之前的方法相比,测量了实体的多样性(实体熵)、词汇多样性(Self-BLEU)以及与Gold文本的相似性(MAUVE)。 在先前的方法中,只有 AttrPrompt (Yu 等人,2023a,附录 E) 尝试通过将任务反转指令模板化,例如 style, topic, length:min-words 等属性,来提高生成文本的多样性。 ReGen 是唯一使用内容源(但不使用任务反转)的综合方法。 因此,我们认为这是 SynthesizRR 的两个最相关的基线。
我们看到,与 AttrPrompt 相比,ReGen 和 SynthesizRR 都实现了非常高的实体熵,从而强调了内容采购步骤的重要性。 与 SynthesizRR 不同,ReGen 仅使用检索,没有明确的任务反转步骤来使上下文类似于 Gold 文本。 因此,我们观察到,与 SynthesizRR 相比,ReGen 在词汇多样性、MAUVE 和学生准确性方面受到影响。
另一方面,思想链提示(S3)尽管生成了强大的分类数据集(如Table 8 中所示),但仍缺乏词汇多样性和与Gold文本相似。 这也出现在 AttrPrompt 和之前的 FewGen 中。 这为以下假设提供了证据:没有内容来源的合成往往会产生多样性较低的数据集,而仅靠复杂的提示策略无法克服这一点。
最后,我们观察到 SunGen 在 IMDb 上表现出非常高的多样性,该任务涉及生成具有积极或消极情绪的电影评论。 然而,正如叶等人(2022a, 第4.6节)中提到的,ZeroGen不仅仅是零样本生成;作者首先使用提示 Movie: 生成电影,然后将生成的电影名称插入到提示模板中 对电影《<电影>》的正面评价是: 生成 SST-2 示例。 SunGen 从 ZeroGen 生成的数据集开始,并学习实例权重(Gao 等人,2023,第 2.2 节)。 我们假设生成的电影与 SynthesizRR 中检索到的上下文具有相同的目的。
附录 C纳入经过提炼的学生模型的反馈
RQ:为什么 SynthesizRR 可以改进分类数据集综合? 在本节中,我们将仔细研究生成的分类数据集以及它在蒸馏过程中如何影响学生模型的训练动态。
除了最终的准确性之外,我们还考虑了标签保存准确性,这是从任务的“oracle”模型中获得的。 我们通过对 DeBERTa-v3-Large 超参数(Appendix K)运行网格搜索,从 Gold 数据构建此预言机,分割 80% Gold 训练集用于微调,20% 用于验证。 然后,我们测量预言机分类为属于提示目标类别的合成示例的比例。 这表明根据提示,生成的示例与其应该所属的类相一致。
我们期望更好的标签保存意味着更高保真度的训练数据集。 然而,Table 9 显示 FewGen 数据集尽管测试性能较低,但仍具有非常高的标签保留率。 特别是在多类任务上(AG.、ToI、Cat.),FewGen 显示了最高的标签保留率(超过 Gold),但这并不能转化为学生成绩的提高。
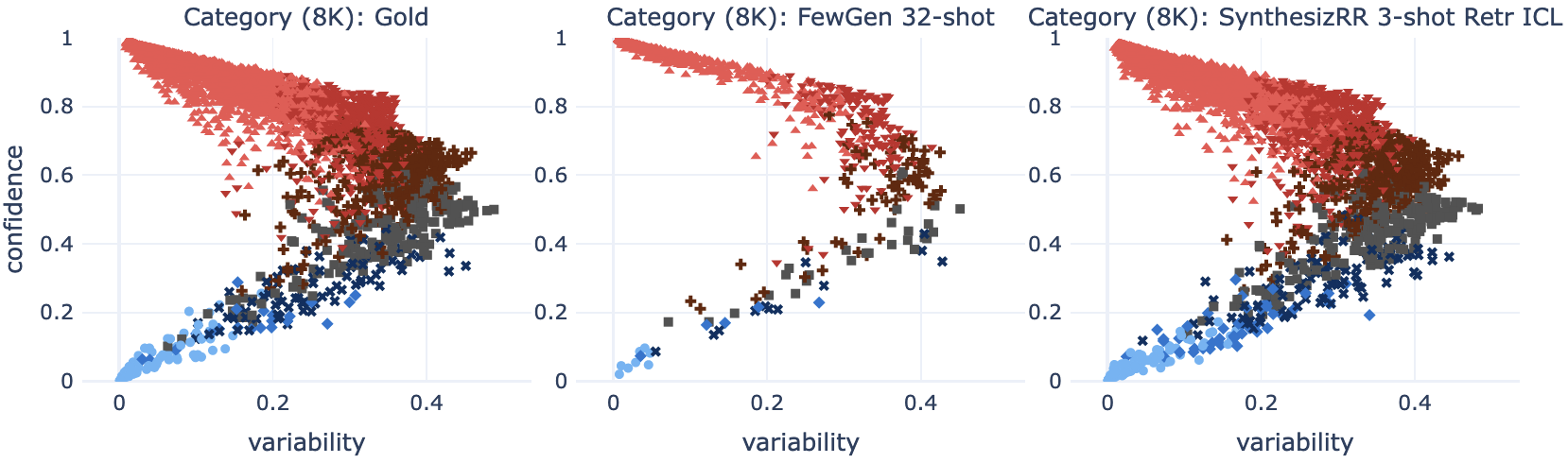
为了理解这一点,我们对多类数据集上的学生训练动态进行了更深入的分析。 我们训练一个 DistilBERT 学生 6 个时期,并绘制相应的数据图 Swayamdipta 等人 (2020)。 对于二进制任务,SynthesizRR 的数据映射与 FewGen 和 Gold 均匹配,但多类的数据映射差异很大。 Figure 5 使用类别任务图说明了这种差异。 从Figure 5 可以清楚地看出,FewGen 代倾向于聚集在易于学习的示例(高置信度和低变异性)周围,而 SynthesizRR包含更多模棱两可的例子(高变异性),Swayamdipta 等人 (2020) 证明这对于学习类别之间的细微差别至关重要。
RQ:我们可以通过利用数据图的学生反馈来提高蒸馏性能吗?
Swayamdipta 等人 (2020) 使用数据图过滤掉易于学习的示例(左上,红色)和可能被错误标记的示例(左下,蓝色),并在人类方面获得卓越的准确性生成的数据集。 我们尝试将相同的技术应用于 SynthesizRR 和 FewGen 生成的合成数据集。
具体来说,我们过滤掉最不模糊的示例(底部 17% 的变异性),并在较小的过滤数据集上重新训练 DistilBERT 学生模型。 在Table 10 中,我们发现 FewGen 性能下降,而 SynthesizRR 性能有所提高(尽管只使用了 83%行)。 我们得出的结论是,SynthesizRR 会生成更多模糊示例,这有助于在多类数据集中建立更好的类可分离性。
| Method | AG. | Hyp. | ToI | Cat. | Hum. | Pol. |
| (Dataset size) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) |
| Gold | ||||||
| LLaMa2 Few shot | ||||||
| FewGen* | 92.4 | 85.9 | 88.1 | |||
| SynzthRR† | 78.6 | |||||
| SynzthRR‡ | 95.7 | 97.6 | ||||
| ClaudeV1 Few shot | ||||||
| FewGen* | 94.5 | 87.4 | 89.4 | |||
| SynzthRR† | 72.8 | 90.7 | ||||
| SynzthRR‡ | 99.7 | |||||
| Method | AG. | ToI | Cat. | Avg | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Dataset size) | (K) | (K) | (K) | |||||
| LLaMa2 Few shot | ||||||||
| FewGen* | 58.0 | 26.2 | 37.6 | 36.1 | 48.0 | 20.6 | 27.6 | |
| SynzthRR† | 85.7 | 2.7 | 76.0 | 2.7 | 74.3 | 1.9 | 2.4 | |
| SynzthRR‡ | 86.3 | 1.1 | 75.0 | 2.2 | 72.9 | 1.0 | 1.4 | |
| ClaudeV1 Few shot | ||||||||
| FewGen* | 71.8 | 4.1 | 72.1 | 0.1 | 69.3 | 0.5 | 1.2 | |
| SynzthRR† | 86.2 | 2.5 | 75.3 | 2.5 | 69.0 | 3.6 | 2.9 | |
| SynzthRR‡ | 86.1 | 2.4 | 74.6 | 2.1 | 70.0 | 2.2 | 2.2 | |
附录 D 使用合成种子集进行引导
SynthesizRR 中的核心假设是存在一小部分人类编写的 任务对种子集。 该种子集至关重要,因为它具有双重目的:它用作检索查询集,并用作上下文学习示例,以指导教师大语言模型在任务反转步骤中的下一个标记分布。
在本节中,我们将考虑如何为资源匮乏的环境合成这样的种子集。 我们的核心假设是种子集很小(二元任务为 100 个/类,多类任务为 50 个/类)。 因此,使用 FewGen 与 top- 和温度 以及三个上下文示例,我们尝试以最少的重复生成多样化的种子集。 当可用的人类数据很少(每类只有 5-15 个示例)或没有可用的人类数据时,这种引导方法使 SynthesizRR 易于处理。
具体来说,我们比较三种范式:
-
1.
真实的零样本: 当我们没有人类数据时,我们利用零样本生成来引导种子集。
-
2.
低资源:在这里,我们假设我们有少量的人类编写的示例,例如每班 5 个示例。 据推测,这不足以直接用作种子集,但我们可以将其用作上下文示例来指导 FewGen 生成器引导实际的种子集。
-
3.
足够:我们不合成种子集。 这是我们在前面几节中探讨过的 SynthesizRR 范例,其中我们的种子集中每个类有 50-100 个 Gold 示例。
正如§4中提到的,真正的零样本范式做出了强有力的假设,但这些假设往往是不必要的限制。 在实践中,获取少量的人类编写的示例(资源不足或种子充足)通常是可行的,但获取数千个人类编写的示例仍然具有挑战性。
| Gold | RetrICL | AG. | Hyp. | ToI | Cat. | Hum. | Pol. | |
| data () | shots | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | |
| Gold | ||||||||
| All | - | 91.0 | 93.2 | 82.5 | 81.5 | 93.1 | 95.3 | |
| True Zero-shot (0-shot FewGen seed) | ||||||||
| None | 0-shot | 66.6 | 68.0 | 60.5 | 60.4 | 76.9 | 76.4 | |
| None | 3-shot | 60.0 | 72.3 | 62.5 | 61.7 | 72.3 | 85.4 | |
| Low-Resource (-shot FewGen seed) | ||||||||
| 5/class | 0-shot | 79.9 | 71.7 | 68.1 | 63.4 | 81.3 | 81.3 | |
| 5/class | 3-shot | 77.7 | 66.8 | 68.9 | 58.8 | 86.4 | 86.5 | |
| 15/class | 0-shot | 78.5 | 72.9 | 69.3 | 65.7 | 77.4 | 84.0 | |
| 15/class | 3-shot | 76.1 | 72.6 | 71.6 | 63.5 | 82.5 | 73.8 | |
| Sufficient (Gold Seed) | ||||||||
| Full seed | 0-shot | 83.5 | 69.8 | 74.5 | 68.9 | 82.5 | 84.7 | |
| Full seed | 3-shot | 83.0 | 78.5 | 73.3 | 72.4 | 90.2 | 91.0 | |
使用合成种子数据运行SynthesizRRRetrICL的结果如Table 11所示。 作为总体趋势,添加更多人工编写的示例会带来更好的性能。 不出所料,最好的结果是在足够的范例中,我们使用 50-100 个 Gold 示例作为检索查询和 RetrICL 集。 真正的零样本结果(没有任何人工输入)要差得多。 然而,令人惊讶的是,我们能够通过每类仅 5 个示例而不是每类完整的 50-100 个示例来获得良好的蒸馏精度,这表明 SynthesizRR 可能在人工注释的资源匮乏的环境中可用数据稀缺。
在低资源范式的某些情况下,我们观察到性能从 0-shot RetrICL 显着下降到 3-shot RetrICL。 我们将此归因于以下事实:即使有 5-15 个 Gold 上下文示例,FewGen 生成的种子集也可能无法反映真正的 Gold 示例(此行为反映在Table 5 中的低 MAUVE 分数中)。 因此,通过在 RetrICL 期间以不正确合成示例为条件,我们将下一个标记分布偏离真实分布。
总之,使用 FewGen 引导种子集可能是在没有足够 Gold 的低资源环境中使用 SynthesizRR 的可行方法任务数据。
附录E检索语料库对域转移的影响
| AG News (K) | ||||||||
| Corpus | DeBERTa () | Mauve () | Self-BLEU-5 () | Entity Ent. () | ||||
| RN/Dom | 85.39 ± 0.8 | 92.58 | 0.23 | 6.72 | ||||
| RN/Rnd | 35.57 ± 6.1 | 83.39 | 0.22 | 7.07 | ||||
| RN/Reg | 84.17 ± 0.7 | 88.88 | 0.26 | 6.72 | ||||
| Hyperpartisan (K) | ||||||||
| Corpus | DeBERTa () | Mauve () | Self-BLEU-5 () | Entity Ent. () | ||||
| RN/Dom | 78.77 ± 2.8 | 66.94 | 0.35 | 6.11 | ||||
| RN/Rnd | 78.77 ± 3.5 | 61.45 | 0.25 | 7.40 | ||||
| RN/Reg | 72.00 ± 2.0 | 65.59 | 0.35 | 6.12 | ||||
我们的期望是,SynthesizRR 可以通过透明地更改检索语料库,同时保持冻结的大语言模型,灵活地将学生专业化到不同的领域。 为了量化更改检索语料库可能如何影响早期指标,我们将新闻语料库切换为 Hyperpartisan 和 AG News。 我们假设RealNews/Dom是最合适的语料库(域内),其他语料库将导致域转移。 在下面的 RQ 中,我们验证了这一假设的成立程度以及信息检索作为 SynthesizRR 中内容来源机制的重要性。
RQ:修改语料库会导致域转移吗? Table 12 发现检索语料库对测试表现(学生指标和内在指标)有很大影响。 当基于具有高度不同实体的语料库(例如 RealNews/Reg)时,所有指标都会显着下降。 因此,我们可以得出结论,替代内容源确实会引起域转移。 域内语料库的紫红色和蒸馏精度最高,而随机检索结果的 Self-BLEU 和实体熵最高。
RQ:检索对于内容采购至关重要吗? 我们通过从域内语料库 RealNews/Dom 中随机选择前 k 个文档来衡量检索的重要性。 我们在Table 12中观察到,使用上下文学习查询进行检索对AG News的性能起着至关重要的作用,因为性能在随机设置中显着下降。 Hyperpartisan不会面临这样的下降。 这符合我们在Table 1中的直觉,即任务倒置对于Hyperpartisan来说是更具挑战性的步骤,并且是一个强大的大语言模型,我们可以将文体变化应用于大多数新闻文章。 在这两种情况下,当实体不再匹配Gold时,紫红色都会受到影响。
RQ:上下文查询是否会检索冗余结果? Figure 6 测量了 200 个 ICL 查询中前 50 个检索到的文档的重叠度,发现在大多数情况下,检索到的文档是唯一的,特别是在使用大型域内语料库时。 因此,我们可以得出结论,有效的检索对于合成数据集的多样性很重要。
RQ:SynthesizRR 能否在相对较小的语料库上有效工作? 在我们的主要结果§5中,我们假设存在一个大型语料库,最小大小为 0.9M 文档。 如前所述,这个语料库不需要是我们任务中未标记的示例;我们能够成功生成针对幽默、类别和极性任务的客户评论和产品问题,同时从产品信息语料库中检索(标题和描述)。
SynthesizRR 的一个潜在问题是如此庞大的语料库数量可能很少。 Thus, we compare the performance of SynthesizRR on CMU Movie Summary Bamman et al. (2013) which is between one to three orders of magnitude smaller than other corpora in Table 6. 在Table 8 中,我们看到 SynthesizRR 即使在相对较小的语料库(42k 电影情节)下也能表现良好。 从之前的 RQ 来看,这表明对于 SynthesizRR 的性能来说,语料库与任务的相关性比语料库的大小更重要。
附录 F SynthesizRR 中的密集检索与稀疏检索
| Retriever | AG. | Hyp. | ToI | Cat. | Hum. | Pol. | Avg. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Size) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | (K) | |
| Gold | 91.0 | 93.2 | 82.5 | 81.5 | 93.1 | 95.3 | 89.43 |
| LLaMa2 Zero shot | |||||||
| Contr. | 83.5 | 69.8 | 74.5 | 68.9 | 82.5 | 84.7 | 77.32 |
| BM25 | 83.2 | 74.2 | 70.7 | 57.6 | 78.5 | 85.4 | 74.93 |
| ClaudeV1 Zero shot | |||||||
| Contr. | 83.9 | 72.3 | 71.8 | 66.8 | 62.1 | 88.7 | 74.29 |
| BM25 | 83.2 | 57.2 | 69.8 | 53.7 | 73.9 | 91.8 | 71.60 |
| LLaMa2 3-shot RetrICL | |||||||
| Contr. | 83.0 | 78.5 | 73.3 | 72.4 | 90.2 | 91.0 | 81.38 |
| BM25 | 82.1 | 77.9 | 71.9 | 65.4 | 87.5 | 87.4 | 78.69 |
| ClaudeV1 3-shot RetrICL | |||||||
| Contr. | 83.7 | 72.3 | 72.8 | 65.4 | 83.4 | 91.3 | 78.16 |
| BM25 | 83.0 | 73.5 | 70.0 | 52.4 | 82.4 | 90.7 | 75.34 |
到目前为止,单个密集检索器(Contriever)已通过使用双编码器方法用于内容采购步骤(Lee 等人,2019;Chen 等人,2017). 我们嵌入输入上下文协变量和每个语料库文档,然后根据余弦相似度对结果进行排名。 在§5中,我们为每个上下文示例检索了文档,并在过滤后,在这些文档中随机采样以生成一组基础文档,我们在其上应用任务反转策略RetrICL。
在本节中,我们探讨改变检索模型如何影响内容采购阶段及其下游影响。 保持流程的其他部分相同,我们将 Contriever 切换为 BM25 Okapi (Robertson 和 Zaragoza,2009),这是一种流行的 稀疏模型检索方法。 像 Contriever 这样的密集检索器在查询和文档之间执行语义匹配,而 BM25 仅执行基于逆术语频率的词汇匹配,而不理解语义。 此外,BM25 输出的分数是无界正数,因此我们无法使用有意义的阈值来限制 RetrICL 方法中的相似性。 相反,我们使用每个 ICL 示例的前 2 个检索到的上下文来构造 RetrICL 上下文内集合,并且不应用过滤器。
我们预计选择语义相似的信息对于 SynthesizRR 来说更为重要,因为我们包含了一个任务反转步骤,该步骤旨在改变文本的语气和词汇结构,同时保留其语义。 因此,我们需要与 Gold 数据语义相关的上下文,我们可以使用任务反转提示对其应用风格或格式转换,使其更接近 Gold。
附录 GRetrICL 中上下文示例的数量不同
正如我们在 §5 中看到的,在 SynthesizRR 的 RetrICL 变体中使用上下文示例可以显着改进内在指标和蒸馏指标。 在这里,我们对不断增加上下文示例的数量是否会产生积极的好处进行了更深入的分析。
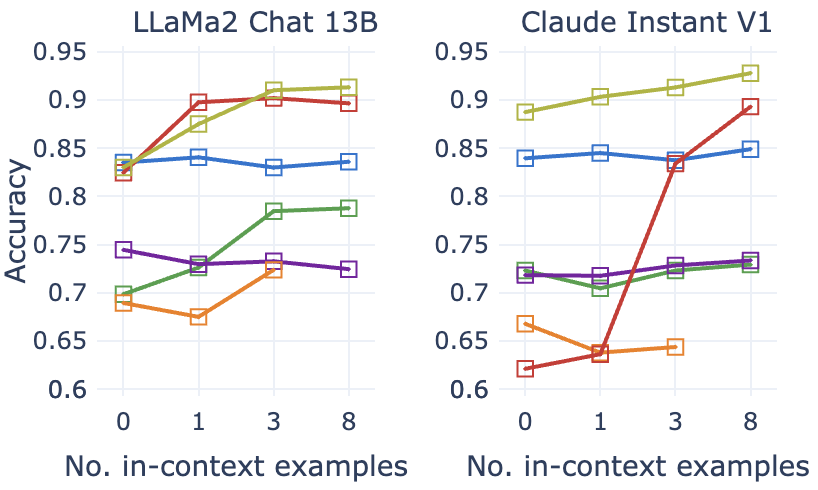
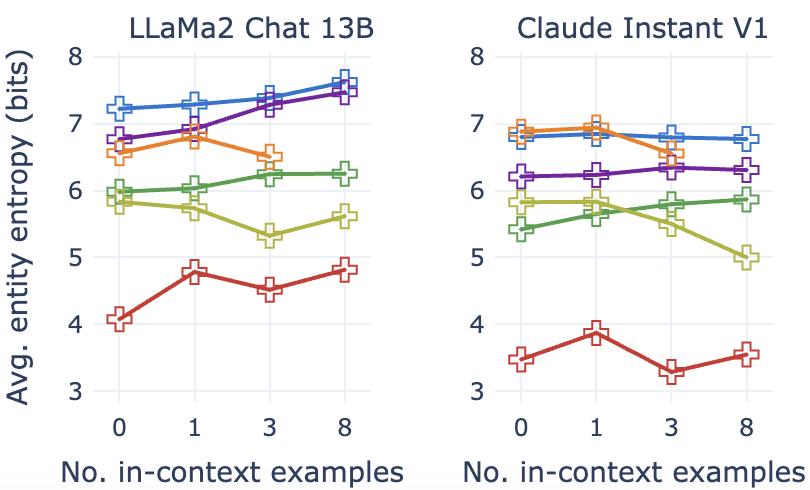
在Figure 7 中,我们查看了具有不同数量的上下文学习示例的数据集的 DeBERTa-v3L 准确性、实体熵和 MAUVE。 我们发现,即使添加一个上下文示例也可以极大地提高所有三个指标的性能。 然而,没有特定数量的上下文示例始终表现出色。 对于 ClaudeV1,添加更多上下文示例(最多 8 个)似乎总是能带来好处,而对于 LLaMa2,我们观察到峰值然后减少。 因此,上下文学习示例的最佳数量是一个依赖于任务的超参数。
附录H任务反转提示和标签语言
在这里,我们讨论用于 FewGen 和 SynthesizRR 任务反转步骤的提示模板和语言。 与目标标签相比,我们使用描述性语言。
此外,在提示中,我们将检索到的文档放置在靠近末尾的位置,因为之前的研究表明中间位置会降低大语言模型的召回率(Liu等人,2023)。
大语言模型对于条件生成有固定的窗口大小,因此过长的文档会被截断(从末尾开始)最多 个标记。 这为上下文学习保留了剩余的窗口。
H.1 超党派
Hyperpartisan 是检测新闻文章中政治偏见的任务。 在将检索到的新闻文章 article_retr[k] 转换为具有此类偏见的新闻文章时,通常会添加嘲讽评论和严厉的政治语言,对人物、政策或政治事件等主题进行深刻批评。 另一方面,相反类别的文章则以中立的语气给出了全面的观点。 我们包含一个长度属性以确保生成一两个段落的长内容。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| true | harsh political language, using a mocking tone and toxic commentary |
| false | neutral language, using a reasonable tone and politically correct commentary |
H.2 ToI 头条
ToI Headlines是印度地区新闻头条的主题分类数据集。 在这里,我们尝试通过将检索到的新闻文章总结为短标题来对其进行细化。 我们使用每节课内容的语言表达,因为这里的示例生成涉及总结内容。 我们添加了“印度”位置属性来指导大语言模型世代将区域化纳入印度次大陆。 包含长度属性以将长度限制为一个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| sports | sports in India |
| life-style | health and lifestyle trends in India |
| education | Indian examinations and education |
| entertainment | the Indian entertainment industry |
| business | business-related developments in India |
| city | ongoing matters in any Indian city |
| environment | environment-related events in Indian cities |
| tech | technology news and the tech industry in India |
| elections | elections and politics in India |
| world | international news and events outside of India |
H.3 AG新闻
我们将 AG News 数据集的任务反转视为新闻摘要的生成。 我们不指定位置修饰符,因为大多数Gold摘要来自美国新闻。 我们添加一个长度属性来限制输出一两个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| Business | companies, industries, markets, trade, investments, entrepreneurship, economic policies, and other business-related developments |
| World | international news, such as politics, diplomacy, conflicts, global events, international relations, human rights issues, and significant global trends |
| Sci/Tech | scientific discoveries, technological advancements, innovations, research breakthroughs |
| Sports | professional sports leagues, major tournaments, athletes, teams, match results, player transfers, coaching changes, sports-related controversies |
H.4 类别
在Category数据集中,我们根据用户在主要电子商务网站上撰写的有关产品的评论来确定产品类别。 对于SynthesizRR中的任务反演,我们必须检索产品并提示冻结的大语言模型在与检索查询相同的产品类别内生成用户评论。 因此,我们包含一个样式属性,以允许生成中出现较小的拼写错误,并使用长度属性将其限制为几个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| magazines | magazines or periodicals covering various topics |
| camera_photo | photography gear including cameras, lenses, accessories, or photo editing tools |
| office_products | office supplies or equipment for professional and home office setups |
| kitchen | kitchenware, appliances, or culinary tools for cooking and dining |
| cell_phones_service | cell phone service accessories or service plans for communication and connectivity |
| computer_video_games | computers, gaming consoles, video games, or related accessories |
| grocery_and_gourmet_food | groceries, fruits and vegetables, gourmet treats, or specialty food items |
| tools_hardware | tools, hardware, or equipment for DIY projects and home repairs |
| automotive | auto parts, accessories, or tools for vehicle maintenance and enhancements |
| music_album | music albums spanning various genres and artists |
| health_and_personal_care | healthcare products, personal care items, or wellness essentials |
| electronics | electronic devices, gadgets, personal tech, or home electronics |
| outdoor_living | products for outdoor activities, gardening, or patio living |
| video | movies, TV shows, and documentaries spanning various genres and artists |
| apparel | clothing including casual wear, formal attire, seasonal outfits, activewear, or fashion accessories for men, women, and children |
| toys_games | fun or educational toys and games for kids of all ages |
| sports_outdoors | products for various sports and outdoor activities |
| books | books in various genres and formats |
| software | computer software for productivity or gaming covering either personal or professional needs |
| baby | baby essentials, gear, or toys for infants and toddlers |
| musical_and_instruments | musical instruments, accessories, or music production equipment |
| beauty | beauty products, cosmetics, or skincare essentials, makeup, hair care, fragrances, or grooming essentials |
| jewelry_and_watches | watches or jewelry pieces such as necklaces, bracelets, earrings, or rings, crafted in precious metals or adorned with gemstones for special occasions |
H.5 幽默
提出幽默的产品问题是对大语言模型任务反转能力的挑战,因为它必须从检索到的产品中产生有趣的问题。 并不是所有的产品都具有明显的幽默特征,因此生成需要一定的匠心。 我们将输出限制为仅问题,以防止大语言模型产生解释或无关的产品。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| humorous | humorous |
| non_humorous | solemn |
H.6 极性
Polarity 是针对主要电子商务网站上的产品评论的情感分类任务。 在SynthesizRR中,难度增加了,因为我们必须从产品生成评论。 对于任务反转,我们提示大语言模型生成评论,该评论可以有积极或消极的情绪,并包括检索到的产品的详细信息。 与类别一样,我们允许拼写错误,并在提示中使用长度属性将长度限制为几个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| positive | what the reviewer liked about the product, how the reviewer found it easy to use the product, or the reviewer’s positive experience with the product |
| negative | what the reviewer disliked about the product, how the reviewer found it challenging to use the product, or the reviewer’s negative experience with the product |
H.7 IMDb
IMDb 是一个评论情感分类任务。 与其他评论任务一样,在任务反转步骤中,我们提示大语言模型生成积极或消极情绪的评论。 SynthesizRR 使用的上下文是来自 CMU Movie Summary 的电影情节。 与类别和极性一样,我们允许拼写错误,并在提示中使用长度属性将长度限制为几个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| positive | what the reviewer liked about the movie |
| negative | what the reviewer disliked about the movie |
H.8SST-2
SST-2 是另一个评论情感分类任务,但示例是从电影评论中提取的部分句子,其中包含情感丰富的短语。 在任务倒转过程中,我们提示教师大语言模型生成积极或消极情绪的部分评论句子。 SynthesizRR 使用的上下文是来自 CMU Movie Summary 的电影情节。 我们允许拼写错误,并使用提示中的长度属性将长度限制为一个句子。
| Label | Verbalization |
|---|---|
| positive | what the reviewer liked about the movie |
| negative | what the reviewer disliked about the movie |
附录一示例生成
在这里,我们展示了性能最佳的 SynthesizRR 方法的示例(使用 LLaMa-2 Chat 13B 的 3 次 Non-RetrICL)。 6 个任务。 为简洁起见,我们不显示 ICL 示例,仅显示检索到的文章和生成的文本。
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: Gov. Andrew Cuomo Wednesdy afternoon staged a press conference to blast federal immigration officials, threatening to sue if agents don’t stop what he described as "reckless and unconstitutional enforcement" practices. Immigration and Customs Enforcement Deputy Director Thomas D. Homan responded hours later with a six-paragraph statement that accused Cuomo of "grandstanding." Cuomo cited a raid last week on a farm in Rome, N.Y. Immigration and Customs Enforcement agents entered John Collins’ property and detained a worker, Marcial DeLeon Aguilar, without presenting a warrant to Collins. That worker was later arrested and is still being detained. "The reckless and unconstitutional practices ICE is deploying in our communities violate everything we believe in New York and are an assault on our democracy," Cuomo said in a prepared statement. "I demand ICE immediately cease and desist this pattern of conduct, and if they fail to do so, I will pursue all available legal recourse and commit to doing everything in my power to protect the rights and safety of all New Yorkers." At about 7:30 p.m., Homan issued this response: "As a native New Yorker who began my law enforcement career as a police officer in the state, I was disappointed to learn about the Governor’s grandstanding today over the issue of immigration enforcement. The Governor’s comments were inaccurate and an insult to ICE’s sworn law enforcement officers who conduct their lawful mission professionally and with integrity. These brave men and woman leave the safety of their homes every day to protect this great nation and our communities. |
| hyperpartisan | What a joke! Governor Andrew Cuomo had the audacity to call out ICE agents for doing their jobs, and now he’s threatening to sue them? Give me a break! The nerve of this guy, talking about "reckless and unconstitutional enforcement" practices when his own state is infested with illegal immigrants who are committing crimes left and right. Cuomo is just trying to grandstand and pander to his liberal base, but the fact is, he’s failing to protect the citizens of New York. ICE agents are just doing their jobs, and they deserve respect for their hard work and dedication. Cuomo should be ashamed of himself for attacking these brave men and women. And let’s not forget, this is the same guy who is protecting child rapists and allowing them to roam free in his state. What a disgrace! Cuomo needs to focus on the real problems in his state, like the rampant crime and corruption, instead of trying to score political points by attacking ICE agents. It’s pathetic. |
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: This week on "Watters’ World", Jesse Watters caught up with several House Democrats who boycotted President Trump’s inauguration, including Rep. John Lewis, the Atlanta Democrat who called the Republican’s election "not legitimate". Approaching Houston Congresswoman Sheila Jackson Lee, Watters asked why she was absent from the festivities: "I have a statement on record, thank you so very much," Jackson Lee said. WATCH: Watters Tracks Down Rep. John Lewis to Ask About Trump Criticism ’Watters’ World’ EXCLUSIVE: Jesse Visits Scene of Chicago Hate Crime Attack Watters Confronts Man Who Harassed Ivanka Trump on JFK Flight As Watters introduced himself as a Fox News reporter to Rep. John Conyers of Michigan, the Detroiter kept walking toward an open elevator, "no, sir, not right now." "I didn’t boycott it, I just didn’t go to it," Conyers said. Rep. Jerrold Nadler of New York gave a similar answer when asked, "for the reasons I stated publicly; they’re on the record." Asked if he was being divisive, the Manhattan Democrat said that if anyone wanted to unite the country, they would not have voted for Trump. Lewis told Watters he was late and couldn’t speak with him as he walked with a quick gait down a hallway. An aide obstructed Watters’ cameraman as the Congressman continued toward his destination. |
| non-hyperpartisan | In a recent segment on "Watters’ World", Jesse Watters spoke with several members of the House of Representatives about their absence from President Trump’s inauguration. While some members provided brief statements, others declined to comment or did not respond to Watters’ inquiries. Rep. John Lewis, an Atlanta Democrat who had publicly questioned the legitimacy of Trump’s election, was approached by Watters but did not stop to speak with him. Lewis had previously stated that he would not attend the inauguration due to his disagreement with Trump’s presidency. Other members, including Rep. John Conyers of Michigan and Rep. Jerrold Nadler of New York, also declined to comment or did not respond to Watters’ questions. When asked why he did not attend the inauguration, Conyers simply stated that he "didn’t go to it". Nadler, who had publicly stated that he would not attend the inauguration due to his disagreement with Trump’s policies, reiterated that he did not support the President’s election. Watters’ segment sparked a discussion on the perceived divisiveness of the President and the responses of those who did not attend his inauguration. While some argued that the boycott was a form of protest against Trump’s policies and actions, others felt that it was a divisive move that further polarized the country. Regardless of one’s political beliefs, it is important to approach discussions and debates with respect and civility, and to strive for understanding and cooperation in the pursuit of common goals. |
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: New Delhi: First reports of exit poll indicate history in West Bengal and regime change in Kerala while it’s too close to call in Tamil Nadu. An exit poll conducted by Star News television channel has projected Congress-led United Progressive Alliance (UPA)’s victory in West Bengal and Kerala. The survey projects Trinamool Congress - Congress alliance wiping out more than three decades old Left Front government in West Bengal. According to the exit polls telecast in the channel on Tuesday says the TMC and Congress will win 181 and 40 respectively while Left Front will be reduced to 62 from 227. In Kerala, the Congress-led United Democratic Front is expected to win 88 while CPM-led Left Democratic Front will win 49. In Tamil Nadu, AIADMK is projected as winning 110 and ruling DMK will have 124 seats in the 234 member assembly. In a close contest, Tarun Gogoi led Congress has a chance to create history in Assam by returning to power for a third consecutive term,post poll surveys predict. The Headlines Today poll predicts 44 of the 126 seats for Congress in Assam,with potential ally AUDF slated to win 14. |
| elections | Exit Polls predict regime change in Kerala, West Bengal; Tight contest in Tamil Nadu |
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: India’s teen sensation P V Sindhu stormed into the third round of the World Badminton Championship with a straight game victory over Olga Golovanova of Russia in women’s singles match here yesterday Copenhagen: India’s teen sensation PV Sindhu stormed into the third round of the World Badminton Championship with a straight game victory over Olga Golovanova of Russia in women’s singles match here yesterday. PV Sindhu The men’s doubles pair of Manu Attri and Sumeeth Reddy B stunned 15th seeded Japanese duo of Hirokatsu Hashimoto and Noriyasu Hirata 21-19 21-19 in 44 minutes to advance to the third round. Sindhu, seeded 11th, took 40 minutes to prevail over her Russian opponent 21-12 21-17 in the second round match at the Ballerup Super Arena here. She will next take on sixth seeded Yeon Ju Bae of Korea. Sindhu won a total of 42 points as compared to 29 by the Russian girl. The world No. 12 from Hyderabad looked a bit rusty to start with and was initially trailing in the opening game. She was playing the catching-up game till 10-10 before Sindhu managed to reel off four consecutive points and surge ahead to 14-10. There was no looking back after that, as Sindhu swiftly sealed the game in her favour with Golovanova earning just two more points. In the second game, the Russian got her act together and opened up a big lead, moving up to 11-6 at the break. |
| sports | 15-year-old PV Sindhu creates history, enters World Badminton Championship 3rd round |
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: SANTIAGO Nov 14 A magnitude 6.1 earthquake hit central-north Chile on Wednesday, the U.S. Geological Survey said, causing buildings to sway in capital Santiago but causing no damage. The USGS said the quake struck on the coast, 54 miles (88 km) north of Coquimbo, at 4:02 p.m. (1902 GMT). It was initially reported as a magnitude 6.0 quake. Chile’s state emergency office, Onemi, said there were no reports of injuries, disruptions to basic services or infrastructure damage as a result of the tremor. The navy said the quake did not meet the conditions needed to trigger a tsunami. World No.1 copper producer Codelco said its operations were normal, and no mines in the metal-producing country reported damages. Seismically active Chile was battered in February 2010 by an 8.8 magnitude quake and ensuing tsunami, which caused billions in damage and killed hundreds. |
| World | A magnitude 6.1 earthquake hit central-north Chile on Wednesday, causing buildings to sway in capital Santiago but causing no damage, the USGS said. |
| (Retrieved document) | News Article: MONTREAL - Canadian astronaut David Saint-Jacques is bracing for some tense moments during next Monday’s launch of the Soyuz rocket that will send him and two others to the International Space Station. On Oct. 11, a rocket failure forced a Soyuz capsule carrying two astronauts to abort and make an emergency landing. Russia suspended all manned space launches pending an investigation before giving the green light Nov. 1. Saint Jacques spoke to reporters today from the launch site in Kazakhstan where he’s in quarantine. He said the most dangerous part of the six-month mission is the 10-minute Soyuz launch and the six hours that follow before docking. He said half of the last two-and-half years of training was dedicated to his role as Soyuz co-pilot for the trip to the space station. Saint-Jacques, 48, said once at the space station he’ll be able to focus on work and life aboard the outpost. The Canadian astronaut’s first space voyage, with NASA astronaut Anne McClain and Oleg Kononenkoof of the Russian space agency Roscosmos, was originally scheduled to launch Dec. 20. It was moved ahead after Russian authorities concluded their investigation into the failed launch. |
| Sci/Tech | commentary Saint-Jacques says the Soyuz launch is the most dangerous part of the six-month mission but he’s been training for it for half of the last two-and-a-half years. |
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: MSD ASY17296 Wiring Harness Factory Terminated MSD Ignition 6ALN (6430) Wiring Harness ASY17296 New harness with factory crimped connections a perfect item to have as an extra or replacement. |
| camera_photo | I have a MSD Ignition 6ALN (6430) and this wiring harness is a great addition. The factory terminated connections are perfect and make installation a breeze. The harness is well made and will definitely last. I have been using it for a few weeks now and it has performed flawlessly. Highly recommend it to anyone looking for a high quality wiring harness. |
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: Conair Travel Smart 3-Dial Combination Lock (6 Pack) Safely Locks Your Luggage With Tsa Recognized Locks Comes With A Red Inspection Status Feature Travel Sentry Approved |
| apparel | I purchased this lock for a business trip to Europe. I’ve used it several times already and so far, so good. The TSA inspectors have been able to open it without a hitch, which is great! |
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: Keeping Up With The Kardashians - Season 5 Region E! brings viewers back into the sensational and completely unpredictable world of one of televisions favourite families with the fourth season of the hit series Keeping Up with the Kardashians. This season, Khlo and her husband, Los Angeles Lakers star, Lamar Odom, begin their new lives as a married couple. Meanwhile, Kourtney is pregnant and back together with Scott, and Kim and her boyfriend, NFL player Reggie Bush, work on their relationship. Through all this change, the Kardashian family must find ways to evolve and keep their close-knit ties. |
| humorous | Does anyone else notice that this is the only show where you can hear people say things like, "OMG I am totally exhausted, I need to take a nap.? And it’s not considered weird? |
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: Coleman Camper’s Storage Tote Securely organize, store and carry camping gear 23" x 14" x 17" Lightweight 600D polyester construction Multiple pockets and compartments Convenient carry strap The Coleman Camper’s Storage Tote is a great way to store, organize and carry your gear – use it in the garage, in the trunk or RV, and at the campsite. Constructed of reliable, lightweight 600D polyester, the Camper’s Storage measures 23" long, 14" wide and 17" tall. It features multiple pockets and compartments for organizing all your gear, and a convenient carry strap so it’s easy to bring along. |
| non_humorous | is this product big enough for all the camping gear for a family of four? |
| Class | Example |
|---|---|
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: Birth Of Soul 1 No half measures here, but a real statement of intent, particularly with that Volume One tag. 28 cuts that helped define that thing called soul - you can argue the point, but you can’t argue the music. Sublime. |
| positive | This album was the beginning of my love affair with soul music. These tracks are timeless and still sound amazing today. |
| (Retrieved document) | Product details: Beware! the Lies of Satan It’s high time we pull the covers off the enemy and expose him for who he really is, the murderer, destroyer, their, deceiver and biggest liar of all time. In this book , you will begin to discover the truth about our heavenly Father and how you can stand in victory over the devil. |
| negative | The book does not live up to it’s promise. There is no revelation of truth about our heavenly father, or any insight into Satan’s lies. It is simply a polemic diatribe against Satan, with no concrete solutions to any of life’s problems. |
附录J数据预处理
J.1数据集
- •
-
•
ToI Headlines:我们使用来自 https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/DPQMQH 的数据并过滤以下标题10 个主题:{体育、生活方式、教育、娱乐、商业、城市、环境、科技、选举、世界}。 我们随机进行二次采样,以便在训练中每个主题获得 5.2k 行,在测试中每个主题获得 1k 行。
- •
- •
- •
除了ToI Headlines之外,我们还使用原始数据集,如Table 1中提到的随机二次采样。
J.2语料库
-
•
RealNews:我们使用文章文本字段并从https://github.com/rowanz/grover/tree/master/realnews下载数据。
-
•
RealNews/Regional 是 RealNews (Zellers 等人,2019) 的子集。 它包括来自非美国和非欧盟网站的 270 万篇文章。 我们手动检查 RealNews 网站,并识别出 141 个地区新闻网站,总部位于 56 个非美国和非欧盟国家:印度、巴基斯坦、尼日利亚、菲律宾等。 Table 28 中提到了完整列表。
-
•
RealNews/India 进一步过滤,仅包含印度新闻网站。 我们仅使用Table 28 中的“印度”域。
-
•
RealNews/Dominant 是来自总部位于 20 个国家/地区的 1063 个新闻网站(其中超过 位于美国)的剩余 3010 万篇文章。
-
•
产品:我们从https://nijianmo.github.io/amazon/index.html#complete-data提取数据并连接标题和描述。
-
•
CMU 电影摘要:数据来自 https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~ark/personas/,我们在其中使用情节摘要文件。
附录 K 教师和学生超参数
K.1 老师大语言模型超参数
对于 LLaMa-2 Chat 13B,我们使用 HuggingFace 的实现:https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Llama-2-13B-fp16 并以一半的速度运行-精确。
对于 Claude Instant-v1,我们使用 Claude Instant v1.2:https://www.anthropic.com/news/releasing-claude-instant-1-2
我们对所有代都使用批量大小 1,因为我们有很长的上下文,并且遇到了较高批量大小的失败。 我们使用 top-p=0.9 的核采样。
K.2 学生 LM 超参数
我们使用 HuggingFace 中的 DeBERTa-v3-Large 和 DistilBERT 模型:https://huggingface.co/microsoft/deberta-v3-large, https://huggingface.co/distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased
我们对 DeBERTa-v3L 和 DistilBERT 使用与 (Yu 等人, 2023a) 相同的超参数:
-
•
DistilBERT:学习率为 5e-5,gradient_accumulation_steps 为 1,batch_size 32。 我们使用 Adam 优化器,weight_decay 为 1e-4,epsilon 为 1e-6。 我们使用 max_sequence_length 为 512。
-
•
DeBERTa-v3L:学习率为2e-5,gradient_accumulation_steps为8,batch_size 4。 我们使用 Adam 优化器,weight_decay 为 1e-4,epsilon 为 1e-6。 我们使用 max_sequence_length 为 512。
我们对所有学生进行 6 个时期的训练。 继(Yu 等人, 2023a)之后,我们在 6% 的训练步骤中使用热身。
K.3 Oracle 模型超参数
为了训练用于标签保留的 DeBERTa-v3-Large 预言机模型,我们使用了 9 种组合的网格搜索:3 个学习率 {2e-5, 5e-5, 1e-4} by 3 个批次-尺寸{1,4,16}(具有相同的梯度累积)。 我们对 80% 的 Gold 训练 数据进行训练,并使用剩余的 20% 作为验证。
K.4 猎犬
我们使用 HuggingFace 库中的 Contriever:https://huggingface.co/facebook/contriever。
我们通过 512 的批量大小进行嵌入。
附录L计算预算
我们在 AWS 弹性云计算上运行所有模型444https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/ 使用 20 台 p3dn.24xlarge 机器调用 AWS 云服务,托管检索索引并提取学生模型。
L.1信息检索
语料库是我们嵌入的,简单的事情是使用 Faiss 库完成的。555https://faiss.ai/index.html 我们使用 Ray 分布式框架编排 80 个 Contriever 副本666https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/index.html 嵌入 RealNews4> 和 Products5> 语料库各需要
L.2 数据集综合
为了运行 LLaMa-2 Chat 13B 和 Claude Instant-v1,我们调用 AWS Bedrock777https://docs.aws.amazon.com/pdfs/bedrock/latest/APIReference/bedrock-api.pdf 使用 boto3 库80>88https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/index.html。
生成是在 AWS 账户级别 RPM 1600 下完成的,对于 8k 行的数据集大约需要 4 小时。
L.3学生蒸馏
每个 DeBERTa-v3-Large 学生模型在单个 GPU 上的 8k 行上训练 1-3 小时。 每个 DistilBERT 学生模型都会在 1 小时内进行训练,以生成用于数据集描记的数据图。
附录 M许可
我们使用之前已通过各种开放许可证发布的数据集。 具体来说:
M.1数据集
-
•
AG News:自定义许可证,描述于http://groups.di.unipi.it/~gulli/AG_corpus_of_news_articles.html
- •
-
•
Hyperpartisan:取自 SemEval 2019 Task 4,根据 https://zenodo.org/records/1489920 根据 Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License 获得许可
-
•
Humor:社区数据许可协议 – 共享 – 版本 1.0 许可证,按照 https://registry.opendata.aws/humor-detection/
-
•
IMDb:(Maas 等人,2011) 未指定许可证,但已将数据提供用于研究:https://ai.stanford.edu /~amaas/数据/情绪/
-
•
SST-2:(Socher 等人,2013) 未指定许可证,但已将数据提供给研究:https://nlp.stanford .edu/sentiment/treebank.html
M.2语料库
-
•
RealNews:按照 https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1LMAUeUtHNPXO9koyAIlDpvyKsLSYlrBj3rYhC30a7Ak/viewform?edit_requested=true 进行自定义许可。 代码存储库是 Apache License 2.0,按照 https://github.com/rowanz/grover/blob/master/LICENSE
-
•
产品:(Ni等人,2019)未指定许可证,但已将数据提供用于研究:https://nijianmo.github.io /amazon/index.html#complete-data。
-
•
CMU 电影摘要:(Bamman 等人,2013) 未指定许可证,但已在以下位置提供数据以供研究:https://www.cs .cmu.edu/~ark/personas/。